Product Description
Application scope and characteristics:
Greentech International (Xihu (West Lake) Dis.) Co., Ltd is the professional vacuum pump supplier. 2BE1 series water ring vacuum pumps and compressors are the products with high efficiency and economic power, which are manufactured by our company integrating with the advanced technology of the imported products from Germany.
These series products adopt CZPT and single action structure and have many advantages, such as, compact structure, convenient maintenance, reliable running, high efficiency and economic power.
The main characteristics of 2BE1 series products:
All the bearings are the imported products with the brand name of CZPT orNTN for ensuring the precise orientation and the high stability during the working of the pump.
The material of the impeller is QT400 nodular iron or stainless steel for ensuring the stability when the pump works under the rigorous condition and can extend the lifetime of the pump.
The casing is made of steel or stainless steel plates to extend the lifetime of the 2BE1 series pumps.
The shaft bushing is made of stainless steel to improve the lifetime of the pump 5 times than the normal material.
The V-belt pulley (when the pump is driven by the belt) is used the high precise pulley with taper bushing to keep the reliability of the pump and extend its life. And it is also easy to mantle and dismantle.
The coupling is used to drive the pump directly. The flexible part connecting the 2 half coupling is made of polyurethane that makes the pump more reliable.
The unique design to set the separator above the pump saves the space and decreases the noise efficiently.
All the parts are cast by the resin sands that make the pump surface very smooth. It is not necessary to cover the surface of the pumps with putty and gives out the heat efficiently.
The mechanical seals (optional) are used the imported products to avoid the leakage when the pump works for a long time.
| Type | Speed (Drive type) r/min |
Shaft power kW |
Motor power kW |
Motor type |
Limited vacuum mbar |
Weight (Whole set) kg |
||
| Suction capacity | ||||||||
| m 3 /h | m 3 /min | |||||||
| 2BE1 151-0 | 1450(D) 1100(V) 1300(V) 1625(V) 1750(V) |
10.8 7.2 9.2 13.2 14.8 |
15 11 11 15 18.5 |
Y160L-4 Y160M-4 Y160M-4 Y160L-4 Y180M-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
405 300 360 445 470 |
6.8 5.0 6.0 7.4 7.8 |
469 428 444 469 503 |
| 2BE1 152-0 | 1450(D) 1100(V) 1300(V) 1625(V) 1750(V) |
12.5 8.3 10.5 15.0 17.2 |
15 11 15 18.5 22 |
Y160L-4 Y160M-4 Y160L-4 Y180M-4 Y180L-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
465 340 415 510 535 |
7.8 5.7 6.9 8.5 8.9 |
481 437 481 515 533 |
| 2BE1 153-0 | 1450(D) 1100(V) 1300(V) 1625(V) 1750(V) |
16.3 10.6 13.6 19.6 22.3 |
18.5 15 18.5 22 30 |
Y180M-4 Y160L-4 Y180M-4 Y180L-4 Y200L-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
600 445 540 660 700 |
10.0 7.4 9.0 11.0 11.7 |
533 480 533 551 601 |
| 2BE1 202-0 | 970(D) 790(V) 880(v) 1100(V) 1170(V) 1300(V) |
17 14 16 22 25 30 |
22 18.5 18.5 30 30 37 |
Y200L2-6 Y180M-4 Y180M-4 Y200L-4 Y200L-4 Y225S-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
760 590 670 850 890 950 |
12.7 9.8 11.2 14.2 14.8 15.8 |
875 850 850 940 945 995 |
| 2BE1 203-0 | 970(D) 790(V) 880(V) 1100(V) 1170(V) 1300(V) |
27 20 23 33 37 45 |
37 30 30 45 45 55 |
Y250M-6 Y200L-4 Y200L-4 Y225M-4 Y225M-4 Y250M-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
1120 880 1000 1270 1320 1400 |
18.7 14.7 16.7 21.2 22.0 23.3 |
1065 995 995 1080 1085 1170 |
| 2BE1 252-0 | 740(D) 558(V) 660(V) 832(V) 885(V) 938(V) |
38 26 31.8 49 54 60 |
45 30 37 55 75 75 |
Y280M-8 Y200L-4 Y225S-4 Y250M-4 Y280S-4 Y280S-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
1700 1200 1500 1850 2000 2100 |
28.3 20.0 25.0 30.8 33.3 35.0 |
1693 1460 1515 1645 1805 1805 |
| 2BE1 253-0 | 740(D) 560(V) 660(V) 740(V) 792(V) 833(V) 885(V) 938(V) |
54 37 45 54 60 68 77 86 |
75 45 55 75 75 90 90 110 |
Y315M-8 Y225M-4 Y250M-4 Y280S-4 Y280S-4 Y280M-4 Y280M-4 Y315S-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
2450 1750 2140 2450 2560 2700 2870 3571 |
40.8 29.2 35.7 40.8 42.7 45.0 47.8 50.3 |
2215 1695 1785 1945 1945 2055 2060 2295 |
| 2BE1 303-0 | 740(D) 590(D) 466(V) 521(V) 583(V) 657(V) 743(V) |
98 65 48 54 64 78 99 |
110 75 55 75 75 90 132 |
Y315L2-8 Y315L2-10 Y250M-4 Y280S-4 Y280S-4 Y280M-4 Y315M-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
4000 3200 2500 2800 3100 3580 4000 |
66.7 53.3 41.7 46.7 51.7 59.7 66.7 |
3200 3200 2645 2805 2810 2925 3290 |
| 2BE1 305-1 2BE1 306-1 |
740(D) 590(D) 490(V) 521(V) 583(V) 657(V) 743(V) |
102 70 55 59 68 84 103 |
132 90 75 75 90 110 132 |
Y355M1-8 Y355M1-10 Y280S-4 Y280S-4 Y280M-4 Y315S-4 Y315M-4 |
160mbar (-0.085MPa) |
4650 3750 3150 3320 3700 4130 4650 |
77.5 62.5 52.5 55.3 61.2 68.8 77.5 |
3800 3800 2950 3000 3100 3300 3450 |
| 2BE1 353-0 | 590(D) 390(V) 415(V) 464(V) 520(V) 585(V) 620(V) 660(V) |
121 65 70 81 97 121 133 152 |
160 75 90 110 132 160 160 185 |
Y355L2-10 Y280S-4 Y280M-4 Y315S-4 Y315M-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L2-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
5300 3580 3700 4100 4620 5200 5500 5850 |
88.3 59.7 61.7 68.3 77.0 86.7 91.7 97.5 |
4750 3560 3665 3905 4040 4100 4100 4240 |
| 2BE1 355-1 2BE1 356-1 |
590(D) 390(V) 435(V) 464(V) 520(V) 555(V) 585(V) 620(V) |
130 75 86 90 102 115 130 145 |
160 90 110 110 132 132 160 185 |
Y355L2-10 Y280M-4 Y315S-4 Y315S-4 Y315M-4 Y315M-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L2-4 |
160mbar (-0.085MPa) |
6200 4180 4600 4850 5450 5800 6100 6350 |
103.3 69.7 76.7 80.8 90.8 98.3 101.7 105.8 |
5000 3920 4150 4160 4290 4300 4350 4450 |
| 2BE1 403-0 | 330(V) 372(V) 420(V) 472(V) 530(V) 565(V) |
97 110 131 160 203 234 |
132 132 160 200 250 280 |
Y315M-4 Y315M-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L2-4 Y355M2-4 Y355L1-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
5160 5700 6470 7380 8100 8600 |
86.0 95.0 107.8 123.0 135.0 143.3 |
5860 5870 5950 6190 6630 6800 |
| 2BE1 405-1 2BE1 406-1 |
330(V) 372(V) 420(V) 472(V) 530(V) 565(V) |
100 118 140 170 206 235 |
132 160 185 200 250 280 |
Y315M-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L2-4 Y315L2-4 Y355M2-4 Y355L1-4 |
160mbar (-0.085MPa) |
6000 6700 7500 8350 9450 15710 |
100.0 111.7 125.0 139.2 157.5 168.3 |
5980 6070 6200 6310 6750 6920 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Rotary Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Kinetic Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | High Vacuum |
| Work Function: | Pre-Suction Pump |
| Working Conditions: | Wet |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
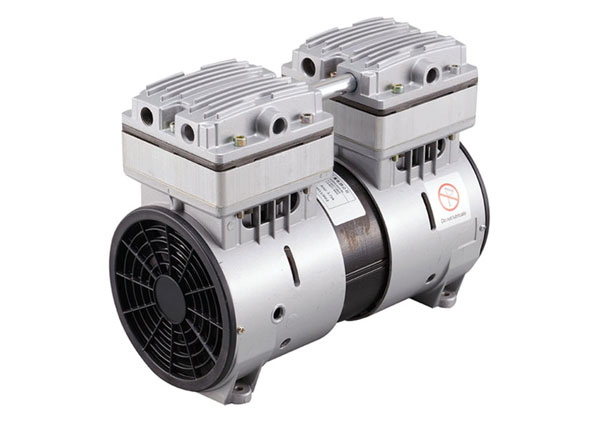

What Are the Advantages of Using Piston Vacuum Pumps?
Piston vacuum pumps offer several advantages that make them suitable for various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of the advantages of using piston vacuum pumps:
1. High Vacuum Levels:
– Piston vacuum pumps are capable of achieving high vacuum levels, making them suitable for applications that require deep vacuum conditions.
– They can create and maintain a vacuum in the range of millitorr (10-3 Torr) to microns (10-6 Torr).
2. Low Flow Rates:
– Piston vacuum pumps are designed to handle low flow rates efficiently.
– They are suitable for applications where a steady and controlled evacuation is required rather than high-volume pumping.
3. Compact and Portable:
– Piston vacuum pumps are relatively compact and lightweight compared to other types of vacuum pumps.
– Their compact design allows for easy installation in limited spaces or portable applications where mobility is required.
4. Oil Lubrication:
– Many piston vacuum pumps utilize oil lubrication for smooth operation and to maintain airtight seals.
– The oil lubrication also helps to cool the pump by dissipating heat generated during operation.
5. Wide Range of Applications:
– Piston vacuum pumps find applications in various industries and processes.
– They are commonly used in laboratories, research facilities, pharmaceutical production, vacuum drying, vacuum filtration, and other applications that require moderate vacuum levels and low flow rates.
6. Cost-Effective:
– Piston vacuum pumps are often more cost-effective compared to other high-vacuum pumps such as turbomolecular pumps or cryogenic pumps.
– They provide a reliable and affordable solution for achieving vacuum requirements in many applications.
7. Easy Maintenance:
– Piston vacuum pumps are relatively easy to maintain.
– Regular maintenance tasks include checking and replacing lubricating oil, inspecting and cleaning valves, and ensuring proper sealing.
– Routine maintenance helps to prolong the lifespan of the pump and maintain its performance.
8. Durability:
– Piston vacuum pumps are known for their durability and long operational life.
– They are designed to withstand continuous operation and handle demanding vacuum conditions.
– With proper care and maintenance, piston vacuum pumps can provide reliable performance over an extended period.
9. Versatility:
– Piston vacuum pumps can handle a wide range of gases, including inert gases, corrosive gases, and vapors.
– This versatility makes them suitable for diverse applications in different industries.
In summary, the advantages of using piston vacuum pumps include their ability to achieve high vacuum levels, handle low flow rates, compact and portable design, oil lubrication for smooth operation, wide range of applications, cost-effectiveness, easy maintenance, durability, and versatility. These advantages make piston vacuum pumps a popular choice in various industries where moderate vacuum levels and controlled evacuation are required.
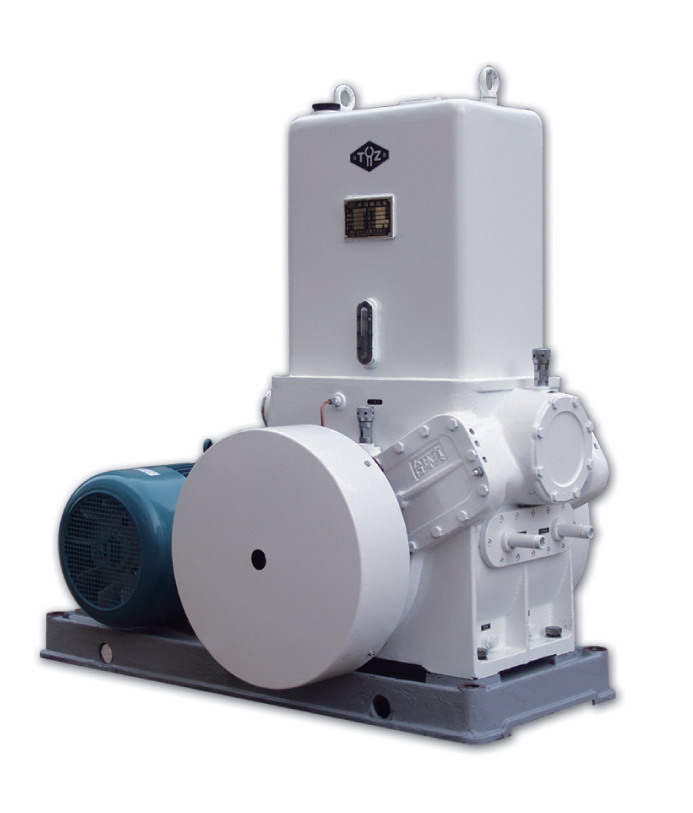

How Does the Cost of Piston Vacuum Pumps Compare to Other Types?
The cost of piston vacuum pumps can vary depending on factors such as the pump’s size, capacity, features, and the specific manufacturer or supplier. Here’s a detailed explanation of how the cost of piston vacuum pumps compares to other types:
– Piston vacuum pumps generally fall into the mid to high range in terms of cost compared to other types of vacuum pumps.
– Compared to rotary vane pumps, which are another common type of vacuum pump, piston pumps are often more expensive.
– This higher cost can be attributed to several factors:
– Design and Construction: Piston vacuum pumps typically have a more complex design and construction, involving precision machining and tighter tolerances. This can contribute to higher manufacturing costs.
– Performance and Features: Piston pumps often offer higher performance and greater pumping capacity compared to other types of pumps. They may also incorporate additional features such as variable speed control or advanced control systems, which can increase the cost.
– Robustness and Durability: Piston pumps are known for their durability and ability to handle demanding applications. They are designed to withstand high pressures and heavy-duty operation, which can contribute to their higher cost.
– On the other hand, when compared to more specialized or advanced vacuum pump technologies such as turbomolecular pumps or cryogenic pumps, piston vacuum pumps are generally more cost-effective.
– Turbomolecular pumps, which are used in high-vacuum applications, are typically more expensive due to their complex design, high rotational speeds, and advanced materials used.
– Cryogenic pumps, which rely on extremely low temperatures for vacuum creation, are also typically more expensive due to the specialized cooling systems and cryogenic components involved.
– It’s important to note that the cost of any vacuum pump can also vary depending on factors such as the required pumping capacity, ultimate vacuum level, and specific industry or application requirements.
– When considering the cost of a piston vacuum pump, it is crucial to assess the overall value it provides in terms of performance, reliability, durability, and suitability for the intended application.
– Additionally, factors such as maintenance requirements, energy efficiency, and the availability of spare parts and service support should also be taken into account when evaluating the cost-effectiveness of a piston vacuum pump.
In summary, piston vacuum pumps generally fall into the mid to high range in terms of cost compared to other types of vacuum pumps. While they may be more expensive than rotary vane pumps, they are often more cost-effective compared to specialized technologies such as turbomolecular pumps or cryogenic pumps. The specific cost of a piston vacuum pump can vary based on factors such as size, capacity, features, and manufacturer.
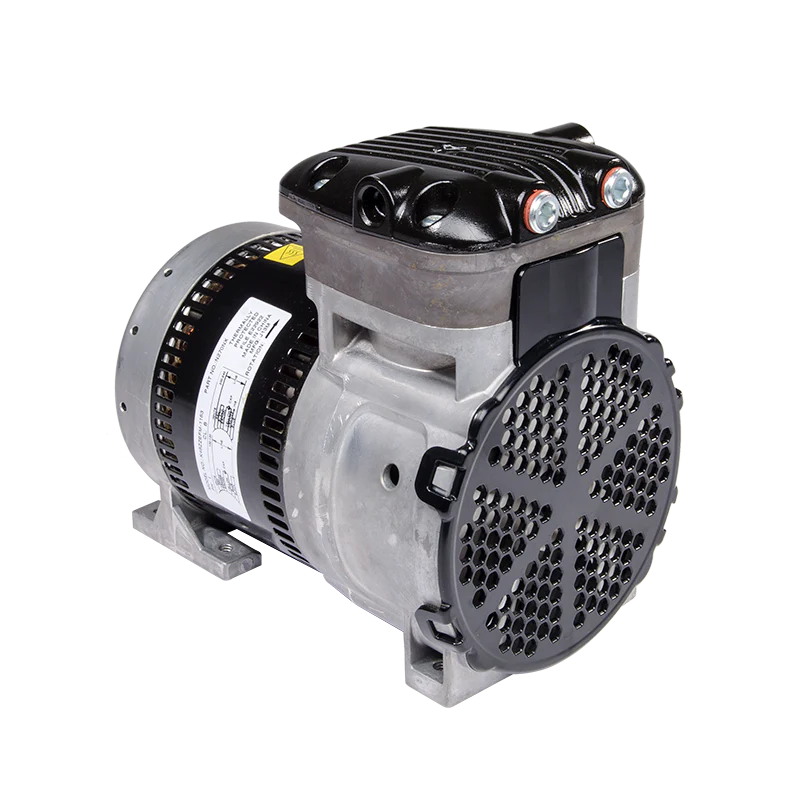

Are There Oil-Free Piston Vacuum Pump Options Available?
Yes, there are oil-free piston vacuum pump options available. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Oil-Free Technology:
– Traditional piston vacuum pumps use oil as a lubricant and sealant in their operation.
– However, advancements in vacuum pump technology have led to the development of oil-free piston vacuum pumps.
– Oil-free piston pumps are designed to operate without the need for lubricating oil, eliminating the risk of oil contamination and the need for oil changes.
2. Dry Running Operation:
– Oil-free piston vacuum pumps achieve lubrication and sealing through alternative means.
– They often utilize materials such as self-lubricating polymers or advanced coatings on the piston and cylinder surfaces.
– These materials reduce friction and provide sufficient sealing to maintain vacuum levels without the need for oil.
3. Applications:
– Oil-free piston vacuum pumps are suitable for a wide range of applications where oil contamination is a concern.
– They are commonly used in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceutical, electronics, laboratories, and medical where a clean and oil-free vacuum environment is required.
4. Advantages:
– The primary advantage of oil-free piston vacuum pumps is their ability to provide a clean and oil-free vacuum.
– They eliminate the risk of oil contamination, which is crucial in sensitive applications such as semiconductor manufacturing or pharmaceutical production.
– Oil-free pumps also simplify maintenance since there is no need for oil changes or regular oil monitoring.
5. Considerations:
– While oil-free piston vacuum pumps offer advantages, they also have some considerations to keep in mind.
– They may have slightly lower ultimate vacuum levels compared to oil-lubricated pumps.
– The absence of oil as a lubricant may result in slightly higher operating temperatures and increased wear on piston and cylinder surfaces.
– It’s important to select an oil-free piston vacuum pump that is suitable for the specific application requirements and consider the trade-offs between performance, cost, and maintenance.
6. Alternative Pump Technologies:
– In some cases, where oil-free operation is critical or specific vacuum levels are required, alternative pump technologies may be more suitable.
– Dry screw pumps, claw pumps, or scroll pumps are examples of oil-free pump technologies that are widely used in various industries.
– These pumps offer oil-free operation, high pumping speeds, and can achieve lower vacuum levels compared to oil-free piston pumps.
In summary, oil-free piston vacuum pumps are available as an alternative to traditional oil-lubricated pumps. They provide a clean and oil-free vacuum environment, making them suitable for applications where oil contamination is a concern. However, it’s important to consider specific application requirements and explore alternative pump technologies if necessary.


editor by Dream 2024-04-17
China high quality Vakuum Pumpe Air Rotary Roots Liquid-Ring Water Piston Dry Portable Mini Scroll Reciprocating Diaphragm Centrifugal Positive Displacement DC AC Vacuum Pumps vacuum pump electric
Product Description
Vakuum Pumpe Air Rotary Roots Liquid-Ring Water Piston Dry Portable Mini Scroll Reciprocating Diaphragm Centrifugal Positive Displacement DC AC Vacuum Pumps
VP roots vacuum pump is in the 50 Torr-micron high vacuum range has a large pumping speed and low cost of equipment, it can be combined with various vacuum pump consists of a vacuum unit. KMBD roots vacuum pump with 5 point bearing design unique, sealing the five bit machine, sealing double sealing structure + mechanical seal for Teflon maze, can realize non leakage, reduce maintenance and repair of the link, ensure the roots pump and durable. Synchronous helical gear and mounted on the driving end, both to ensure quiet and reliable operation, and can reduce the load of the rotor torque. Impeller and shaft integrally cast, can provide large size shaft, impeller and reduce the risk of damage. All contact with the sealing surface of the shaft end faces are polished to reduce wear and reduce the risk of leakage, high temperature high pressure casing, and double tank design, a variety of material selection, further to ensure that the use of the user in various working conditions. Typical application: chemical, petrochemical, plastics, semiconductors, wood mixture, food processing, vacuum furnace, vacuum booster system, vacuum drying, vacuum dewatering, vacuum packaging
Typical Applications
Special structures working principles,suitable for operation in chemical industry,oil industry,food industry,electrical utility industry,pharmacy industry,textile industry and paper making industry,etc. The other industries that need vacuum drying,concentration,distilling,dehydration and filtering also need the water-ring vacuum pump. It can be use as a backing pump of Roots Pump.
Specifications
| Model | Capacity | Ultimate Pressure | Power | speed |
| L/S | Pa | KW | RPM | |
| VP200 | 200 | 0.05 | 4 | 2900 |
| VP600 | 600 | 0.05 | 7.5 | 2900 |
Characteristic Curves
Overall Dimensions
company information
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Oil or Not: | Optional |
|---|---|
| Inlet Diam. (mm): | 100/200mm |
| Motor Power (Kw): | 4/7.5 Kw |
| Ultimate Pressure (PA): | 0.05 |
| Transport Package: | Wooden Case |
| Trademark: | OEM |
| Samples: |
US$ 999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

What Are the Key Components of a Piston Vacuum Pump?
A piston vacuum pump consists of several key components that work together to create a vacuum. Here’s a detailed explanation of these components:
1. Cylinder:
– The cylinder is a cylindrical chamber where the piston moves back and forth.
– It provides the housing for the piston and plays a crucial role in creating the vacuum by changing the volume of the chamber.
2. Piston:
– The piston is a movable component that fits inside the cylinder.
– It creates a seal between the piston and cylinder walls, allowing the pump to create a pressure differential and generate a vacuum.
– The piston is typically driven by a motor or an external power source.
3. Intake Valve:
– The intake valve allows gas or air to enter the cylinder during the suction stroke.
– It opens when the piston moves downward, creating a vacuum and drawing gas into the cylinder from the system being evacuated.
4. Exhaust Valve:
– The exhaust valve allows the expelled gas to exit the cylinder during the compression stroke.
– It opens when the piston moves upward, allowing the compressed gas to be expelled from the cylinder.
5. Lubrication System:
– Piston vacuum pumps often incorporate a lubrication system to ensure smooth operation and maintain an airtight seal between the piston and cylinder walls.
– Lubricating oil is introduced into the cylinder to provide lubrication and help maintain the seal.
– The lubrication system also helps to cool the pump by dissipating heat generated during operation.
6. Cooling System:
– Some piston vacuum pumps may include a cooling system to prevent overheating.
– This can involve the circulation of a cooling fluid or the use of cooling fins to dissipate heat generated during operation.
7. Pressure Gauges and Controls:
– Pressure gauges are often installed to monitor the vacuum level or pressure within the system.
– Control mechanisms, such as switches or valves, may be present to regulate the operation of the pump or maintain the desired vacuum level.
8. Motor or Power Source:
– The piston in a piston vacuum pump is typically driven by a motor or an external power source.
– The motor provides the necessary mechanical energy to move the piston back and forth, creating the suction and compression strokes.
9. Frame or Housing:
– The components of the piston vacuum pump are housed within a frame or housing that provides structural support and protection.
– The frame or housing also helps to reduce noise and vibration during operation.
In summary, the key components of a piston vacuum pump include the cylinder, piston, intake valve, exhaust valve, lubrication system, cooling system, pressure gauges and controls, motor or power source, and the frame or housing. These components work together to create a vacuum by reciprocating the piston within the cylinder, allowing gas to be drawn in and expelled, while maintaining an airtight seal. The lubrication and cooling systems, as well as pressure gauges and controls, ensure smooth and efficient operation of the pump.
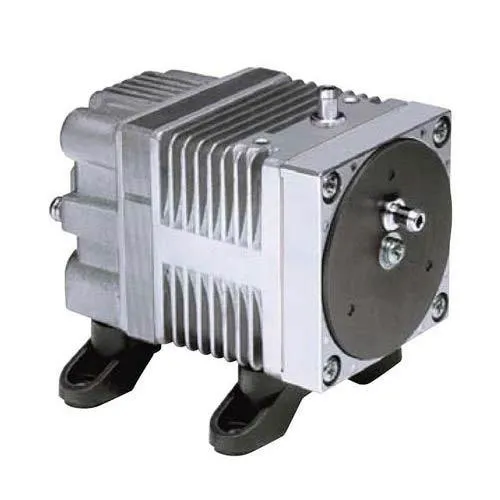

How Do You Troubleshoot Common Issues with Piston Vacuum Pumps?
Troubleshooting common issues with piston vacuum pumps involves a systematic approach to identify and resolve problems. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Insufficient Vacuum Level:
– If the vacuum level achieved by the piston pump is lower than expected:
– Check for leaks: Inspect all connections, seals, and fittings for any signs of leakage. Repair or replace any damaged components.
– Verify valve operation: Ensure that the valves in the pump are functioning correctly. Clean or replace any faulty valves that may be impeding the pump’s performance.
– Check for worn piston or cylinder: Examine the piston and cylinder for signs of wear. If necessary, replace these components to restore optimal vacuum performance.
2. Excessive Noise or Vibrations:
– If the piston pump is producing excessive noise or vibrations:
– Check for misalignment: Ensure that the pump is properly aligned with its drive mechanism. Adjust or realign as necessary.
– Inspect mounting and support: Examine the pump’s mounting and support structure to ensure it is stable and secure. Reinforce or repair any weak or damaged mounts.
– Verify lubrication: Adequate lubrication is crucial for smooth pump operation. Check the lubrication system and ensure it is supplying sufficient lubricant to all necessary components.
3. Overheating:
– If the piston pump is overheating:
– Check cooling system: Inspect the cooling system, including fans, heat exchangers, and cooling fins. Clean or replace any clogged or malfunctioning cooling components.
– Verify airflow: Ensure that there is proper airflow around the pump. Remove any obstructions or debris that may be impeding the flow of cooling air.
– Evaluate operating conditions: Examine the pump’s operating conditions, such as ambient temperature and duty cycle. Adjust these factors if necessary to prevent overheating.
4. Oil Contamination:
– If there is oil contamination in the vacuum system:
– Check oil seals: Inspect the seals in the pump for any signs of damage or wear. Replace any faulty seals that may be allowing oil leakage.
– Verify oil level and quality: Ensure that the pump’s oil level is correct and that the oil is clean and free from contaminants. Replace the oil if necessary.
– Evaluate oil mist separation: If the pump is equipped with oil mist separation mechanisms, verify their effectiveness. Clean or replace any filters or separators that may be compromised.
5. Insufficient Pumping Capacity:
– If the pump is unable to meet the required pumping capacity:
– Check for blockages: Inspect the intake and exhaust ports for any blockages or obstructions. Clear any debris or foreign objects that may be impeding the pump’s operation.
– Verify valve operation: Ensure that the valves are opening and closing properly. Clean or replace any valves that may be stuck or malfunctioning.
– Evaluate motor performance: Assess the motor driving the pump for any issues such as insufficient power or improper speed. Repair or replace the motor if necessary.
6. Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
– It’s important to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and documentation for specific troubleshooting procedures and recommendations tailored to the particular piston vacuum pump model.
– Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for routine maintenance, inspections, and any specific troubleshooting steps provided.
In summary, troubleshooting common issues with piston vacuum pumps involves steps such as checking for leaks, verifying valve operation, inspecting for wear or misalignment, ensuring proper lubrication and cooling, addressing oil contamination, clearing blockages, and evaluating motor performance. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines and documentation is essential for accurate troubleshooting and resolving problems effectively.
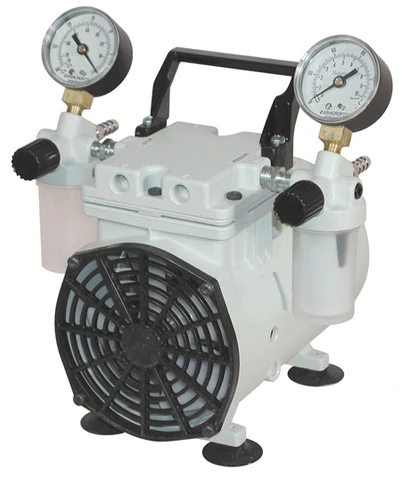

Can Piston Vacuum Pumps Handle Corrosive Gases or Vapors?
Piston vacuum pumps are generally not suitable for handling corrosive gases or vapors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Construction Materials:
– Piston vacuum pumps are typically constructed with materials such as cast iron, aluminum, stainless steel, and various elastomers.
– While these materials offer good resistance to normal operating conditions, they may not be compatible with corrosive substances.
– Corrosive gases or vapors can attack and degrade the pump’s internal components, leading to reduced performance, increased wear, and potential failure.
2. Sealing and Contamination:
– Piston vacuum pumps rely on tight seals and clearances to maintain the vacuum and prevent leakage.
– Corrosive gases or vapors can degrade the seals and compromise their effectiveness.
– This can result in increased leakage, reduced pumping efficiency, and potential contamination of the pump and the surrounding environment.
3. Maintenance and Service:
– Handling corrosive gases or vapors requires specialized knowledge, materials, and maintenance procedures.
– The pump may need additional protective measures, such as corrosion-resistant coatings or specialized seal materials, to withstand the corrosive environment.
– Regular inspection, cleaning, and replacement of components may also be necessary to maintain the pump’s performance and prevent damage.
4. Alternative Pump Options:
– If corrosive gases or vapors are involved in the application, it is advisable to consider alternative pump technologies that are specifically designed to handle such substances.
– For corrosive gases, chemical-resistant pumps like diaphragm pumps, peristaltic pumps, or dry screw pumps may be more suitable.
– These pumps are constructed with materials that offer superior resistance to corrosion and can handle a wide range of corrosive substances.
– It is essential to consult the pump manufacturer or a vacuum system specialist to select the appropriate pump for handling corrosive gases or vapors.
In summary, piston vacuum pumps are generally not recommended for handling corrosive gases or vapors due to their construction materials, sealing limitations, and the potential for damage and contamination. It is crucial to choose a pump specifically designed to handle corrosive substances or consider alternative pump technologies that can provide the required chemical resistance and performance.


editor by CX 2024-04-16
China wholesaler Vakuum Pumpe Air Rotary Roots Liquid-Ring Water Piston Dry Portable Mini Scroll Reciprocating Diaphragm Centrifugal Positive Displacement DC AC Vacuum Pumps vacuum pump design
Product Description
Vakuum Pumpe Air Rotary Roots Liquid-Ring Water Piston Dry Portable Mini Scroll Reciprocating Diaphragm Centrifugal Positive Displacement DC AC Vacuum Pumps
VP roots vacuum pump is in the 50 Torr-micron high vacuum range has a large pumping speed and low cost of equipment, it can be combined with various vacuum pump consists of a vacuum unit. KMBD roots vacuum pump with 5 point bearing design unique, sealing the five bit machine, sealing double sealing structure + mechanical seal for Teflon maze, can realize non leakage, reduce maintenance and repair of the link, ensure the roots pump and durable. Synchronous helical gear and mounted on the driving end, both to ensure quiet and reliable operation, and can reduce the load of the rotor torque. Impeller and shaft integrally cast, can provide large size shaft, impeller and reduce the risk of damage. All contact with the sealing surface of the shaft end faces are polished to reduce wear and reduce the risk of leakage, high temperature high pressure casing, and double tank design, a variety of material selection, further to ensure that the use of the user in various working conditions. Typical application: chemical, petrochemical, plastics, semiconductors, wood mixture, food processing, vacuum furnace, vacuum booster system, vacuum drying, vacuum dewatering, vacuum packaging
Typical Applications
Special structures working principles,suitable for operation in chemical industry,oil industry,food industry,electrical utility industry,pharmacy industry,textile industry and paper making industry,etc. The other industries that need vacuum drying,concentration,distilling,dehydration and filtering also need the water-ring vacuum pump. It can be use as a backing pump of Roots Pump.
Specifications
| Model | Capacity | Ultimate Pressure | Power | speed |
| L/S | Pa | KW | RPM | |
| VP200 | 200 | 0.05 | 4 | 2900 |
| VP600 | 600 | 0.05 | 7.5 | 2900 |
Characteristic Curves
Overall Dimensions
company information
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Oil or Not: | Optional |
|---|---|
| Inlet Diam. (mm): | 100/200mm |
| Motor Power (Kw): | 4/7.5 Kw |
| Ultimate Pressure (PA): | 0.05 |
| Transport Package: | Wooden Case |
| Trademark: | OEM |
| Samples: |
US$ 999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
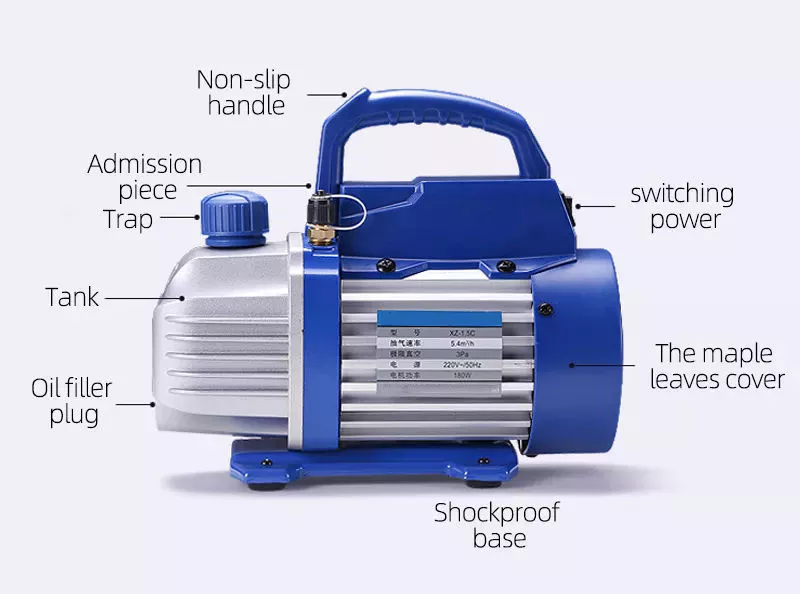
Basic knowledge of vacuum pump
A vacuum pump is a device that draws gas molecules from a sealed volume and maintains a partial vacuum. Its main job is to create a relative vacuum within a given volume or volumes. There are many types of vacuum pumps. This article will describe how they work, their types, and their applications.
How it works
A vacuum pump is a mechanical device that removes gas from a system by applying it to a higher pressure than the surrounding atmosphere. The working principle of the vacuum pump is based on the principle of gas transfer and entrapment. Vacuum pumps can be classified according to their vacuum level and the number of molecules that can be removed per cubic centimeter of space. In medium to high vacuum, viscous flow occurs when gas molecules collide with each other. Increasing the vacuum causes molecular or transitional flow.
A vacuum pump has several components that make it a versatile tool. One of the main components is the motor, which consists of a rotor and a stator. The rotor and stator contain coils that generate a magnetic field when excited. Both parts must be mounted on a base that supports the weight of the pump. There is also an oil drain that circulates oil throughout the system for lubrication and cooling purposes.
Another type of vacuum pump is the liquid ring vacuum pump. It works by positioning the impeller above or below the blades. Liquid ring pumps can also adjust the speed of the impeller. However, if you plan to use this type of pump, it is advisable to consult a specialist.
Vacuum pumps work by moving gas molecules to areas of higher or lower pressure. As the pressure decreases, the removal of the molecules becomes more difficult. Industrial vacuum systems require pumps capable of operating in the 1 to 10-6 Torr range.
Type
There are different types of vacuum pumps. They are used in many different applications, such as laboratories. The main purpose of these pumps is to remove air or gas molecules from the vacuum chamber. Different types of pumps use different techniques to achieve this. Some types of pumps use positive displacement, while others use liquid ring, molecular transfer, and entrapment techniques.
Some of these pumps are used in industrial processes, including making vacuum tubes, CRTs, electric lights, and semiconductor processing. They are also used in motor vehicles to power hydraulic components and aircraft. The gyroscope is usually controlled by these pumps. In some cases, they are also used in medical settings.
How a vacuum pump works depends on the type of gas being pumped. There are three main types: positive displacement, negative displacement, and momentum transfer. Depending on the type of lubrication, these principles can be further divided into different types of pumps. For example, dry vacuum pumps are less sensitive to gases and vapors.
Another type of vacuum pump is called a rotary vane pump. This type of pump has two main components, the rotor and the vacuum chamber. These pumps work by rotating moving parts against the pump casing. The mating surfaces of rotary pumps are designed with very small clearances to prevent fluid leakage to the low pressure side. They are suitable for vacuum applications requiring low pulsation and high continuous flow. However, they are not suitable for use with grinding media.
There are many types of vacuum pumps and it is important to choose the right one for your application. The type of pump depends on the needs and purpose of the system. The larger ones can work continuously, and the smaller ones are more suitable for intermittent use. 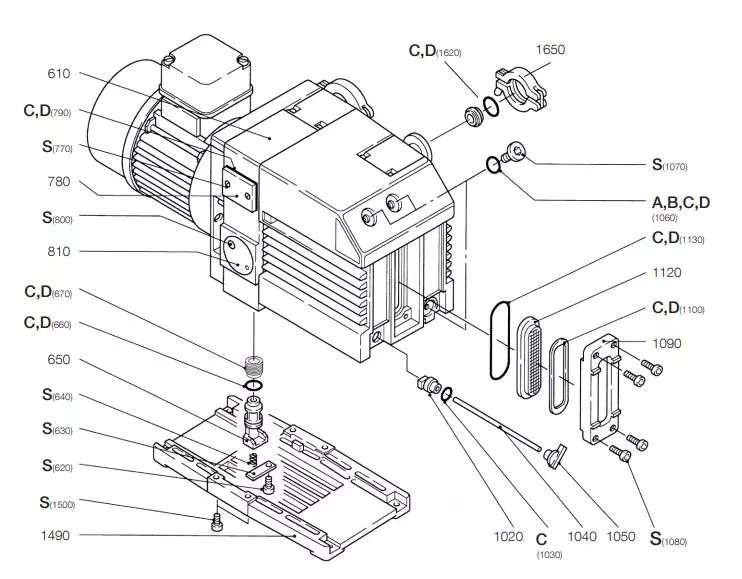
Apply
Vacuum pumps are used in a variety of industrial and scientific processes. For example, they are used in the production of vacuum tubes, CRTs, and electric lamps. They are also used in semiconductor processing. Vacuum pumps are also used as mechanical supports for other equipment. For example, there may be multiple vacuum pumps on the engine of a motor vehicle that powers the hydraulic components of an aircraft. In addition, they are often used in fusion research.
The most common type of vacuum pump used in the laboratory is the rotary vane pump. It works by directing airflow through a series of rotating blades in a circular housing. As the blades pass through the casing, they remove gas from the cavity and create a vacuum. Rotary pumps are usually single or double-stage and can handle pressures between 10 and 6 bar. It also has a high pumping speed.
Vacuum pumps are also used to fabricate solar cells on wafers. This involves a range of processes including doping, diffusion, dry etching, plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition, and bulk powder generation. These applications depend on the type of vacuum pump used in the process, and the vacuum pump chosen should be designed for the environment.
While there are several types of vacuum pumps available, their basic working principles remain the same. Each has different functions and capacities, depending on the type of vacuum. Generally divided into positive displacement pump, rotary vane pump, liquid ring pump, and molecular delivery pump.
Maintenance
The party responsible for general maintenance and repairs is the Principal Investigator (PI). Agknxs must be followed and approved by the PI and other relevant laboratory personnel. The Agknx provides guidelines for routine maintenance of vacuum pump equipment. Agknxs are not intended to replace detailed routine inspections of vacuum pump equipment, which should be performed by certified/qualified service personnel. If the device fails, the user should contact PI or RP for assistance.
First, check the vacuum pump for any loose parts. Make sure the inlet and outlet pressure gauges are open. When the proper pressure is shown, open the gate valve. Also, check the vacuum pump head and flow. Flow and head should be within the range indicated on the label. Bearing temperature should be within 35°F and maximum temperature should not exceed 80°F. The vacuum pump bushing should be replaced when it is severely worn.
If the vacuum pump has experienced several abnormal operating conditions, a performance test should be performed. Results should be compared to reference values to identify abnormalities. To avoid premature pump failure, a systematic approach to predictive maintenance is essential. This is a relatively new area in the semiconductor industry, but leading semiconductor companies and major vacuum pump suppliers have yet to develop a consistent approach.
A simplified pump-down test method is proposed to evaluate the performance of vacuum pumps. The method includes simulated aeration field tests and four pump performance indicators. Performance metrics are evaluated under gas-loaded, idle, and gas-load-dependent test conditions. 
Cost
The total cost of a vacuum pump consists of two main components: the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs. The latter is the most expensive component, as it consumes about four to five times the initial investment. Therefore, choosing a more energy-efficient model is a good way to reduce the total system cost and payback period.
The initial cost of a vacuum pump is about $786. Oil-lubricated rotary vane pumps are the cheapest, while oil-free rotary vane pumps are slightly more expensive. Non-contact pumps also cost slightly more. The cost of a vacuum pump is not high, but it is a factor that needs careful consideration.
When choosing a vacuum pump, it is important to consider the type of gas being pumped. Some pumps are only suitable for pumping air, while others are designed to pump helium. Oil-free air has a different pumping rate profile than air. Therefore, you need to consider the characteristics of the medium to ensure that the pump meets your requirements. The cost of a vacuum pump can be much higher than the purchase price, as the daily running and maintenance costs can be much higher.
Lubricated vacuum pumps tend to be more durable and less expensive, but they may require more maintenance. Maintenance costs will depend on the type of gas that needs to be pumped. Lighter gases need to be pumped slowly, while heavier gases need to be pumped faster. The maintenance level of a vacuum pump also depends on how often it needs to be lubricated.
Diaphragm vacuum pumps require regular maintenance and oil changes. The oil in the diaphragm pump should be changed every 3000 hours of use. The pump is also resistant to chemicals and corrosion. Therefore, it can be used in acidic and viscous products.


editor by CX 2024-04-04
China Best Sales Whc Solar Pump for Deep Well Rotary Piston Vacuum Pump Water Cooling Pump supplier
Product Description
WHC SOLAR System Solar Pump Inverter Solar Power 60-90V DC Water Pump Solar Surface Water Pump
Model: WHC550-48-24-6PM
Product Name: Solar Surface PM Water Pump System
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
| Overview | |
| Product Name | Solar Surface PM Water Pump System |
| Model | WHC550-48-24-6PM |
| Max Head | 24m |
| Rate Head | 16m |
| Max Flow Rate | 6000L/H |
| Rated Flow Rate | 4000L/H |
| Specifications | |
| Solar Panel | High Efficiency Mono 120W*8PCS |
| Motor power | 550W |
| Mppt Controller | 48V15A |
| Woking Time | Daytime |
| Application | River,Lake,Pool,Irrigation,Home |
| Outlet Inch | 1″ |
| Speed of motor | 2850r/min |
| Material of pump | Steel |
PRODUCT FEATURES
| Related Information | |
| CBM/Set | 0.25 |
| Weight(kg)/Set | 81 |
| Solar Input (Voc) | <100V |
| Solar Input Range (Vmp) | 60-90V |
| Theory | Centrifugal Pump |
| Impeller | Plastic-steel ,Scerw |
| Working principle | DC Brushless |
| Feature | High Efficiency;Long life |
| Pressure | High Pressure |
| Controller Protection Class | IP65 |
SYSTEM APPLICATIONS
TECHNICAL PARAMETERS
HOT SALE PRODUCTS
COMPANY PROFILE
FACTORY STRENGTH
CERTIFICATE DISPLAY
PACKING & DELIVERY
FAQ
Q1. MOQ& Samples.
A: MOQ is 1 PC. Welcome sample order to test and check quality. Customized is available.
Q2. What about the lead time?
A: Samples within 10 days, big order within 4 weeks.
Q3. How do you ship the goods?
A: By sea. We have MSDS,test report for safe transport and non-dangerous products.
Q4. Is it OK to print my logo on product?
A: Yes. Free logo print.
Q5. Do you offer guarantee for the products?
A: Yes. We offer 1-3 years’ warranty to our products. The time depends on the goods model.
Q6. How to deal with the faulty?
A: Firstly, our products are produced in strict quality control system and the defective rate will be less than 0.01%.Secondly, during the warranty period, we will repair or replace defected products.
Q7. Are you manufacturer or trading company?
A: Manufacturer. Factory is located in ZheJiang province. Show room is located in HangZhou.
Q8. If we could accept OEM &ODM Service?
Accept customized, such as the brand, Logo, Container color etc.
Thank you for your read!
Website:whc-solar.en.Made-in-China.com
If you have any doubt please no hesitate to contact me, we are sure any your question will get our prompt reply.
We look CZPT to establish business relationship with you!
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Yes |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 3 Years |
| Condition: | New |
| Certification: | ISO, CE, RoHS |
| Application: | Home, Industrial, Commercial, Outdoor |
| Specification: | Normal, 550W 48V 24M 6PM |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
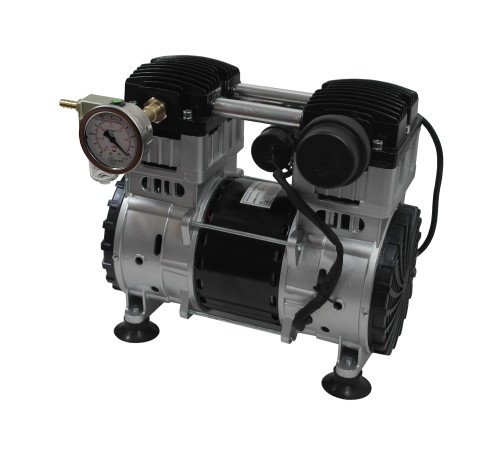

How Does Piston Displacement Affect the Pump’s Performance?
Piston displacement is a crucial factor that significantly affects the performance of a piston vacuum pump. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Piston displacement refers to the volume of gas or air that a piston vacuum pump can move during each stroke of the piston. It determines the pump’s capacity or flow rate, which is the amount of gas that the pump can evacuate per unit of time.
1. Flow Rate:
– The piston displacement directly influences the flow rate of the pump.
– A larger piston displacement corresponds to a higher flow rate, meaning the pump can evacuate a larger volume of gas per unit of time.
– Conversely, a smaller piston displacement results in a lower flow rate.
2. Pumping Speed:
– The pumping speed is a measure of how quickly a vacuum pump can remove gas molecules from a system.
– The piston displacement is directly related to the pumping speed of the pump.
– A larger piston displacement leads to a higher pumping speed, allowing for faster evacuation of the system.
– A smaller piston displacement results in a lower pumping speed, which may require more time to achieve the desired vacuum level.
3. Vacuum Level:
– The piston displacement indirectly affects the achievable vacuum level of the pump.
– A larger piston displacement can help reach lower pressures and achieve a deeper vacuum.
– However, it’s important to note that achieving a deep vacuum also depends on other factors such as the design of the pump, the quality of the seals, and the operating conditions.
4. Power Consumption:
– The piston displacement can impact the power consumption of the pump.
– A larger piston displacement typically requires more power to operate the pump due to the increased volume of gas being moved.
– Conversely, a smaller piston displacement may result in lower power consumption.
5. Size and Weight:
– The piston displacement affects the size and weight of the pump.
– A larger piston displacement generally requires a larger pump size and may increase the weight of the pump.
– On the other hand, a smaller piston displacement can result in a more compact and lightweight pump.
It’s important to select a piston vacuum pump with an appropriate piston displacement based on the specific application requirements.
In summary, the piston displacement of a vacuum pump directly influences its flow rate, pumping speed, achievable vacuum level, power consumption, and size. Understanding the relationship between piston displacement and pump performance is crucial in choosing the right pump for a given application.
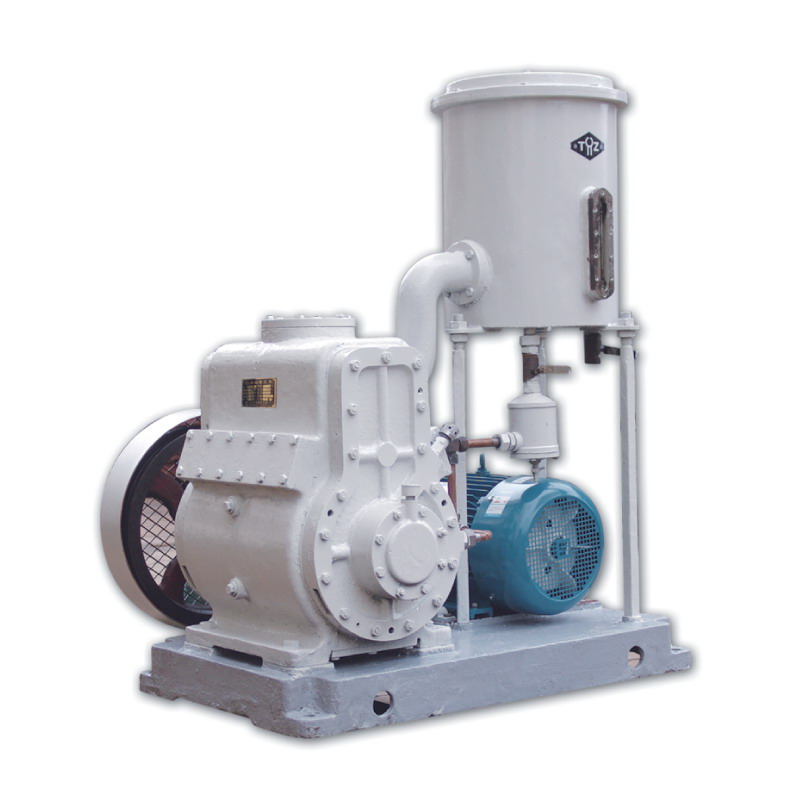

Can Piston Vacuum Pumps Be Used in Medical or Pharmaceutical Applications?
Yes, piston vacuum pumps can be used in medical and pharmaceutical applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
– Piston vacuum pumps are versatile and widely used in various industries, including medical and pharmaceutical sectors.
– Medical and pharmaceutical applications often require vacuum technology for processes such as filtration, degassing, drying, and sample preparation.
– Piston vacuum pumps offer several advantages that make them suitable for these applications:
– High Vacuum Levels: Piston pumps can achieve high vacuum levels, which are often necessary in medical and pharmaceutical processes that require precise control and removal of gases or vapors.
– Contamination-Free Operation: Piston pumps can provide contamination-free operation, making them suitable for applications where maintaining a sterile or clean environment is crucial, such as in pharmaceutical manufacturing or medical research laboratories.
– Oil-Free Operation: Some piston vacuum pumps are designed to operate without oil lubrication. Oil-free pumps eliminate the risk of oil contamination in sensitive medical or pharmaceutical processes and avoid the need for oil changes or maintenance associated with oil-lubricated pumps.
– Quiet Operation: Piston pumps can be engineered to operate with reduced noise levels, which is advantageous in medical and pharmaceutical settings where a quiet working environment is desired.
– Durability and Reliability: Piston pumps are known for their robust construction and durability, allowing them to withstand demanding applications and provide reliable performance over extended periods.
– Compact Size: Piston vacuum pumps are available in compact designs, making them suitable for applications where space is limited, such as in medical devices or portable pharmaceutical equipment.
– Some specific medical and pharmaceutical applications where piston vacuum pumps are commonly used include:
– Vacuum Filtration: Piston pumps are used to generate the necessary vacuum for filtering solutions or suspensions in laboratory or industrial settings. This process is often employed in pharmaceutical research, production of vaccines, or purification of drugs.
– Freeze Drying: Piston vacuum pumps assist in the freeze-drying process, which is a common technique used in the pharmaceutical industry to preserve and stabilize sensitive drugs or biological samples.
– Vacuum Packaging: Piston pumps are utilized for creating a vacuum in packaging processes where maintaining product quality and extending shelf life are critical, such as in the pharmaceutical packaging of medicines or medical devices.
– Laboratory Evaporation: Piston vacuum pumps are employed in laboratory applications for the evaporation of solvents or liquids in medical or pharmaceutical research, drug development, or quality control processes.
– It is important to select the appropriate piston vacuum pump model based on the specific requirements of the medical or pharmaceutical application. Factors to consider include vacuum level needed, flow rate, compatibility with the handled substances, and compliance with industry regulations and standards.
– Additionally, compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other regulatory guidelines is crucial when using piston vacuum pumps in medical or pharmaceutical applications to ensure product safety, quality, and regulatory compliance.
In summary, piston vacuum pumps are suitable for use in medical and pharmaceutical applications due to their ability to achieve high vacuum levels, provide contamination-free and oil-free operation, offer quiet and reliable performance, and accommodate compact design requirements. They are commonly used in processes such as vacuum filtration, freeze drying, vacuum packaging, and laboratory evaporation in these industries.

Can Piston Vacuum Pumps Handle Corrosive Gases or Vapors?
Piston vacuum pumps are generally not suitable for handling corrosive gases or vapors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Construction Materials:
– Piston vacuum pumps are typically constructed with materials such as cast iron, aluminum, stainless steel, and various elastomers.
– While these materials offer good resistance to normal operating conditions, they may not be compatible with corrosive substances.
– Corrosive gases or vapors can attack and degrade the pump’s internal components, leading to reduced performance, increased wear, and potential failure.
2. Sealing and Contamination:
– Piston vacuum pumps rely on tight seals and clearances to maintain the vacuum and prevent leakage.
– Corrosive gases or vapors can degrade the seals and compromise their effectiveness.
– This can result in increased leakage, reduced pumping efficiency, and potential contamination of the pump and the surrounding environment.
3. Maintenance and Service:
– Handling corrosive gases or vapors requires specialized knowledge, materials, and maintenance procedures.
– The pump may need additional protective measures, such as corrosion-resistant coatings or specialized seal materials, to withstand the corrosive environment.
– Regular inspection, cleaning, and replacement of components may also be necessary to maintain the pump’s performance and prevent damage.
4. Alternative Pump Options:
– If corrosive gases or vapors are involved in the application, it is advisable to consider alternative pump technologies that are specifically designed to handle such substances.
– For corrosive gases, chemical-resistant pumps like diaphragm pumps, peristaltic pumps, or dry screw pumps may be more suitable.
– These pumps are constructed with materials that offer superior resistance to corrosion and can handle a wide range of corrosive substances.
– It is essential to consult the pump manufacturer or a vacuum system specialist to select the appropriate pump for handling corrosive gases or vapors.
In summary, piston vacuum pumps are generally not recommended for handling corrosive gases or vapors due to their construction materials, sealing limitations, and the potential for damage and contamination. It is crucial to choose a pump specifically designed to handle corrosive substances or consider alternative pump technologies that can provide the required chemical resistance and performance.


editor by CX 2024-04-03
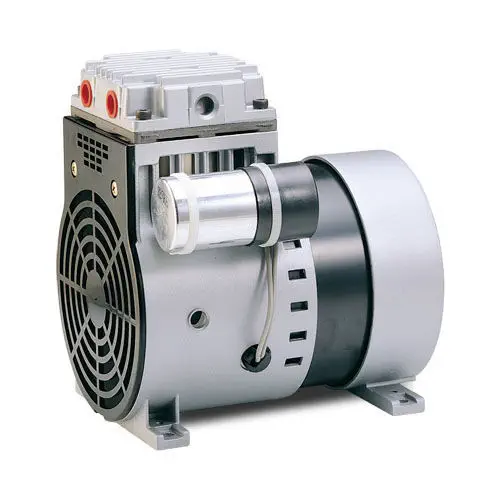
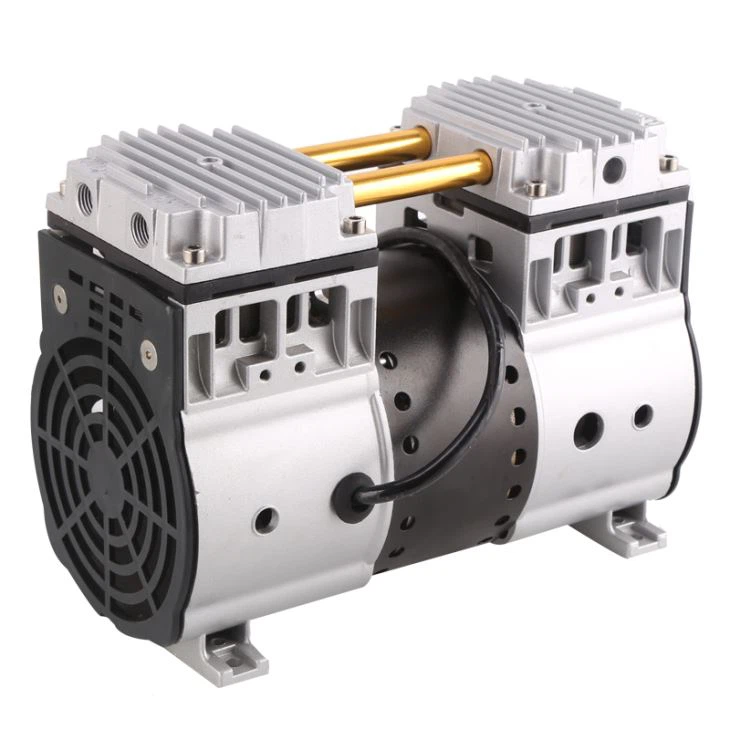
China best Industrial Screw Piston AC Silent Oilless Oil Free Vacuum Low Noise Copper Home Small Highly Portable Rotary Part Mini Air Compressor Pump vacuum pump engine
Product Description
Scope of application:
Using for Pushing Pneumatic Nail Gun, Air Screw , Spray Painting Gun to work, also use to miniature instrument, blowing dust, Air inflation for small car and so on.
Product Feature:
- High Power, high efficiency, low energy, high reliability.
- Piston Ring: New ECO circle, low friction coefficient, Auto lubricating system.
- Cylinder Liner: Surface hardening, deplete hardness, Accelerate the heat transfer, long using time.
- Suction and exhaust valve: Using advanced foreign technology.
- Multiple Pressure: Overload protection
Oilless Air Compressor Featuers:
1.Super Silent
Super low noise.The output air pressure is stable without fluctuations, reducing noise pollution.
2. Safety
If the voltage or current cause the machine overheat, it will automatically shut down to protect from burnout.
3. Automatic control
Pressure switch automatically controls the start and stop of the machine.
4. Adjustable air pressure
The air pressure can be adjusted to meet the needs of different equipment usage.
5. Save human power
Switch on the air compressor can work normally & automatically. It is easy to operate and does not need human to be on duty.
6. Easy maintenance
No need to add any lubricant, easy maintenance after purchase.
Parts Features
1.Heavy cast iron body: heavy load, long stroke, low fuel consumption, low noise
2.Cylinder: made of high-grade cast iron, strength, good lubricity, wall by the fine honing, wear-resistant, durable
3.Piston ring: good elasticity, excellent wear resistance, low oil consumption, not easy to make the valve group carbon deposition and loss of oil to burn the crankshaft and connecting rod.
4.The crankshaft, connecting rod, piston: well balanced, wear resistance, high strength, smooth running balance.
5.High reliable and durable valve; strong aluminum alloy body, light and heat.
6.The motor provides reliable power, low voltage start up and running performance strong fan cooled motor and body; special shock proof design.
7.Double nozzles, were used to direct the exhaust and pressure exhaust; pressure switch with push button, safe and convenient
8.Oil free,silent,protect-environment,suitable for dental use.
Frequency Asked Question
1.Are you the manufacturer or trading company?
We are the manufacturer.
2.Where is your factory?
It is located in HangZhou City,ZHangZhoug Province,China.
3.What’s the terms of trade?
FOB,CFR,CIF or EXW are all acceptable.
4.What’s the terms of payment?
T/T,L/C at sight or cash.
5.What’s the lead time?
We are the manufacturer.
It is located in HangZhou City,ZHangZhoug Province,China.
FOB,CFR,CIF or EXW are all acceptable.
T/T,L/C at sight or cash.
In 15 days on receipt of deposit .
6.Do you accept sample order?
Yes,we accept.
7.What about the cost of sample?
You have to pay the freight charge.But the cost of product could be refundable,if you will purchase 1x20GP container in the future.
Yes,we accept.
You have to pay the freight charge.But the cost of product could be refundable,if you will purchase 1x20GP container in the future.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-less |
|---|---|
| Cooling System: | Air Cooling |
| Cylinder Arrangement: | Duplex Arrangement |
| Cylinder Position: | Vertical |
| Structure Type: | Open Type |
| Compress Level: | Double-Stage |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Types of vacuum pumps
A vacuum pump is a device that draws gas molecules from a sealed volume and leaves a partial vacuum in its wake. Its job is to create a relative vacuum within a specific volume or volume. There are many types of vacuum pumps, including centrifugal, screw and diaphragm.
Forward centrifugal pump
Positive displacement centrifugal vacuum pumps are one of the most commonly used pump types in the oil and gas industry. Their efficiency is limited to a range of materials and can handle relatively high solids concentrations. However, using these pumps has some advantages over other types of pumps.
Positive displacement pumps have an enlarged cavity on the suction side and a reduced cavity on the discharge side. This makes them ideal for applications involving high viscosity fluids and high pressures. Their design makes it possible to precisely measure and control the amount of liquid pumped. Positive displacement pumps are also ideal for applications requiring precise metering.
Positive displacement pumps are superior to centrifugal pumps in several ways. They can handle higher viscosity materials than centrifuges. These pumps also operate at lower speeds than centrifugal pumps, which makes them more suitable for certain applications. Positive displacement pumps are also less prone to wear.
Positive displacement vacuum pumps operate by drawing fluid into a chamber and expanding it to a larger volume, then venting it to the atmosphere. This process happens several times per second. When maximum expansion is reached, the intake valve closes, the exhaust valve opens, and fluid is ejected. Positive displacement vacuum pumps are highly efficient and commonly used in many industries.
Self-priming centrifugal pump
Self-priming centrifugal pumps are designed with a water reservoir to help remove air from the pump. This water is then recirculated throughout the pump, allowing the pump to run without air. The water reservoir can be located above or in front of the impeller. The pump can then reserve water for the initial start.
The casing of the pump contains an increasingly larger channel forming a cavity retainer and semi-double volute. When water enters the pump through channel A, it flows back to the impeller through channels B-C. When the pump is started a second time, the water in the pump body will be recirculated back through the impeller. This recycling process happens automatically.
These pumps are available in a variety of models and materials. They feature special stainless steel castings that are corrosion and wear-resistant. They can be used in high-pressure applications and their design eliminates the need for inlet check valves and intermediate valves. They can also be equipped with long intake pipes, which do not require activation.
Self-priming centrifugal pumps are designed to run on their own, but there are some limitations. They cannot operate without a liquid source. A foot valve or external liquid source can help you start the self-priming pump.
Screw Pump
The mechanical and thermal characteristics of a screw vacuum pump are critical to its operation. They feature a small gap between the rotor and stator to minimize backflow and thermal growth. Temperature is a key factor in their performance, so they have an internal cooling system that uses water that circulates through the pump’s stator channels. The pump is equipped with a thermostatically controlled valve to regulate the water flow. Also includes a thermostatic switch for thermal control.
Screw vacuum pumps work by trapping gas in the space between the rotor and the housing. The gas is then moved to the exhaust port, where it is expelled at atmospheric pressure. The tapered discharge end of the screw further reduces the volume of gas trapped in the chamber. These two factors allow the pump to work efficiently and safely.
Screw vacuum pumps are designed for a variety of applications. In some applications, the pump needs to operate at very low pressures, such as when pumping large volumes of air. For this application, the SCREWLINE SP pump is ideal. Their low discharge temperature and direct pumping path ensure industrial process uptime. These pumps also feature non-contact shaft seals to reduce mechanical wear. Additionally, they feature a special cantilever bearing arrangement to eliminate potential sources of bearing failure and lubrication contamination.
Screw vacuum pumps use an air-cooled screw to generate a vacuum. They are compact, and clean, and have a remote monitoring system with built-in intelligence. By using the app, users can monitor pump performance remotely. 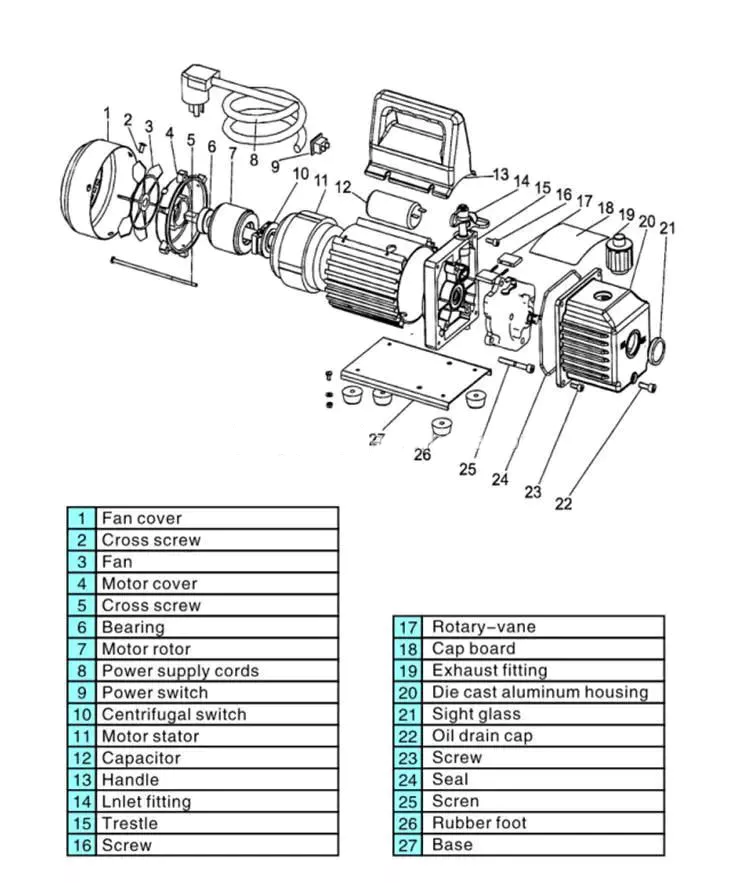
Diaphragm Pump
Diaphragm vacuum pumps are one of the most common types of vacuum pumps found in laboratories and manufacturing facilities. The diaphragm is an elastomeric membrane held in place around the outer diameter. While it is not possible to seal a diaphragm vacuum pump, there are ways to alleviate the problems associated with this design.
Diaphragm vacuum pumps are versatile and can be used in a variety of clean vacuum applications. These pumps are commercially available with a built-in valve system, but they can also be modified to include one. Because diaphragm pumps are so versatile, it’s important to choose the right type for the job. Understanding how pumps work will help you match the right pump to the right application.
Diaphragm vacuum pumps offer a wide range of advantages, including an extremely long service life. Most diaphragm pumps can last up to ten thousand hours. However, they may be inefficient for processes that require deep vacuum, in which case alternative technologies may be required. Additionally, due to the physics of diaphragm pumps, the size of these pumps may be limited. Also, they are not suitable for high-speed pumping.
Diaphragm vacuum pumps are a versatile subset of laboratory pumps. They are popular for their oil-free construction and low maintenance operation. They are available in a variety of styles and have many optional features. In addition to low maintenance operation, they are chemically resistant and can be used with a variety of sample types. However, diaphragm pumps tend to have lower displacements than other vacuum pumps.
Atmospheric pressure is a key factor in a vacuum pump system
Atmospheric pressure is the pressure created by the collision of air molecules. The more they collide, the greater the pressure. This applies to pure gases and mixtures. When you measure atmospheric pressure, the pressure gauge reads about 14.7 psia. The higher the pressure, the greater the force on the gas molecules.
The gas entering the vacuum pump system is below atmospheric pressure and may contain entrained liquids. The mechanism of this process can be explained by molecular kinetic energy theory. The theory assumes that gas molecules in the atmosphere have high velocities. The resulting gas molecules will then start moving in random directions, colliding with each other and creating pressure on the walls of the vacuum vessel.
Atmospheric pressure is a critical factor in a vacuum pump system. A vacuum pump system is useless without proper atmospheric pressure measurement. The pressure in the atmosphere is the total pressure of all gases, including nitrogen and oxygen. Using total pressure instead of partial pressure can cause problems. The thermal conductivity of various gases varies widely, so working at full pressure can be dangerous.
When choosing a vacuum pump, consider its operating range. Some pumps operate at low atmospheric pressure, while others are designed to operate at high or ultra-high pressure. Different types of pumps employ different technologies that enhance their unique advantages. 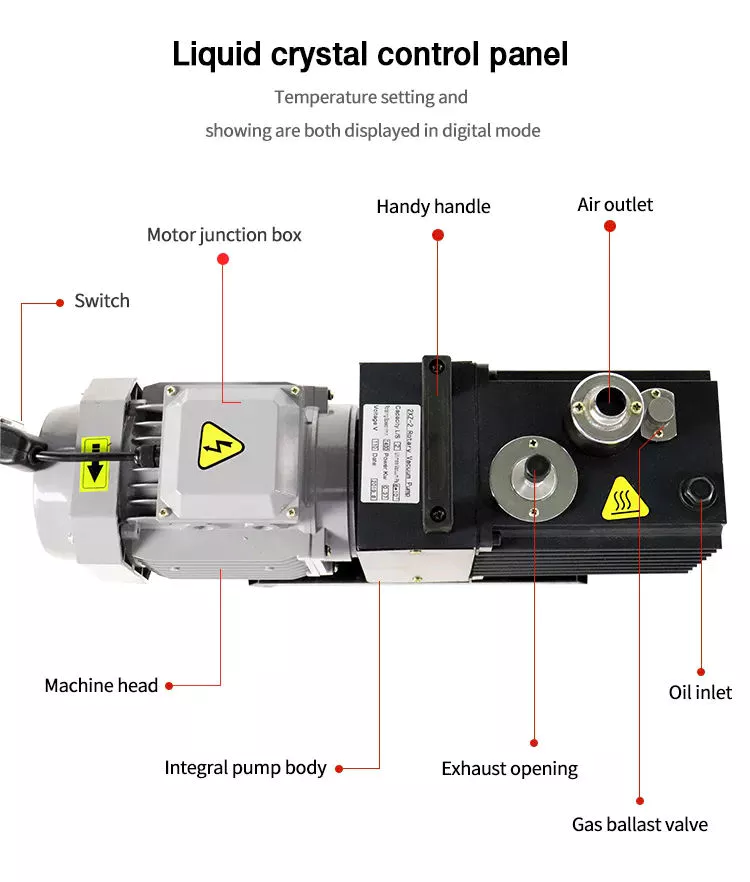
The screw pump is less efficient in pumping gases with smaller molecular weight
Vacuuming requires a high-quality pump. This type of pump must be able to pump gas of high purity and very low pressure. Screw pumps can be used in laboratory applications and are more efficient when pumping small molecular weight gases. Chemical resistance is critical to pump life. Chemical resistant materials are also available. Chemically resistant wetted materials minimize wear.
Gear pumps are more efficient than screw pumps, but are less efficient when pumping lower molecular weight gases. Gear pumps also require a larger motor to achieve the same pumping capacity. Compared to gear pumps, progressive cavity pumps also have lower noise levels and longer service life. In addition, gear pumps have a large footprint and are not suitable for tight spaces.
Progressive cavity pumps have two or three screws and a housing and side cover. They are also equipped with gears and bearings. Their mechanical design allows them to operate in high pressure environments with extremely low noise. The progressive cavity pump is a versatile pump that can be used in a variety of applications.
Dry screw compressors have different aspect ratios and can operate at high and low pressures. The maximum allowable differential pressure for screw compressors ranges from 0.4 MPa for 3/5 rotors to 1.5 MPa for 4/6 rotors. These numbers need to be determined on a case-by-case basis.


editor by CX 2024-04-03
China Professional Boosters Roots Rotary Van Piston Pump Replace 5.5kw Single Double Stage Water Ring Vacuum Pump vacuum pump
Product Description
2BV liquid ring vacuum pump is single-stage monobloc design vacuum pump. It offers Space-saving installation, compared to conventional pumps, the 2BV’s monoblock design delivers the benefits of a simple, compact and economical installation. Since the pump and motor are integral and self supporting, there is no need for additional base plates, couplings or guards, which add to the cost, complexity and overall size of the installation. With CE and Atex certificate, it is an ideal product for much different application including Plastics Industry, Medical Industry, Chemical Industry, Processing Industry, Food and Beverage Industry and other General Industry.
We offer same outline dimensions for bolt-on replacement and equivalent performances with original 2BV liquid ring vacuum pump.
|
ITEM |
UNIT |
Quantity |
|
Supply Ability |
per month |
2,000set |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Online Service |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Oil or Not: | Oil |
| Structure: | Rotary Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Entrapment Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | High Vacuum |
| Samples: |
US$ 10000/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What Are the Typical Applications of Piston Vacuum Pumps?
Piston vacuum pumps find applications in various industries and processes. Here’s a detailed explanation of the typical applications of piston vacuum pumps:
1. Laboratories and Research Facilities:
– Piston vacuum pumps are commonly used in laboratories and research facilities for a wide range of applications.
– They are utilized in vacuum ovens, freeze dryers, vacuum filtration systems, and other equipment requiring controlled evacuation.
2. Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology:
– In the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, piston vacuum pumps are employed for processes such as solvent evaporation, distillation, and filtration.
– They are used in drug manufacturing, vaccine production, and research involving biochemistry and molecular biology.
3. Food Processing and Packaging:
– Piston vacuum pumps play a vital role in the food processing and packaging industry.
– They are used in vacuum packaging machines to remove air from packaging containers, extending the shelf life of food products.
4. HVAC and Refrigeration Systems:
– Piston vacuum pumps are utilized in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems and refrigeration systems.
– They help evacuate air and moisture from the systems to achieve the desired pressure and prevent contamination.
5. Manufacturing and Industrial Processes:
– Piston vacuum pumps are employed in various manufacturing and industrial processes.
– They are used for degassing, vacuum impregnation, vacuum drying, and other applications that require controlled evacuation.
6. Automotive Industry:
– In the automotive industry, piston vacuum pumps are often used in brake booster systems.
– They create a vacuum to assist in brake actuation, providing the necessary power for braking.
7. Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing:
– Piston vacuum pumps are utilized in electronics and semiconductor manufacturing processes.
– They help create a controlled environment with low-pressure conditions during the production of microchips, integrated circuits, and other electronic components.
8. Environmental Monitoring and Analysis:
– Piston vacuum pumps are utilized in environmental monitoring and analysis equipment.
– They are used in air sampling devices, gas analyzers, and other instruments that require precise vacuum control.
9. Scientific Research and Vacuum Systems:
– Piston vacuum pumps are employed in various scientific research applications.
– They are used in vacuum systems for particle accelerators, electron microscopes, mass spectrometers, surface analysis instruments, and other scientific equipment.
In summary, piston vacuum pumps have diverse applications in laboratories, pharmaceuticals, food processing, HVAC systems, manufacturing processes, automotive industry, electronics, environmental monitoring, scientific research, and more. Their ability to provide controlled evacuation and achieve moderate vacuum levels makes them suitable for a wide range of industries and processes.

What Industries Commonly Rely on Piston Vacuum Pumps?
Various industries rely on piston vacuum pumps for their specific applications and requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Manufacturing and Industrial Processes:
– Piston vacuum pumps find extensive use in manufacturing and industrial processes across different sectors.
– They are commonly employed in vacuum packaging, where they help create a vacuum environment to preserve and extend the shelf life of food products.
– In the automotive industry, piston vacuum pumps are utilized in brake booster systems to provide the necessary vacuum for power braking.
– Other industrial applications include vacuum molding, vacuum drying, vacuum distillation, and vacuum filtration.
2. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Industry:
– The pharmaceutical and medical industry extensively relies on piston vacuum pumps for various critical processes.
– These pumps are used in pharmaceutical manufacturing for vacuum drying, solvent recovery, and distillation processes.
– In medical applications, piston vacuum pumps are utilized in vacuum suction devices and medical laboratory equipment.
– They are also employed in vacuum autoclaves for sterilization purposes.
3. Research and Laboratory Settings:
– Piston vacuum pumps are commonly found in research laboratories and scientific facilities.
– They are used for creating vacuum conditions in laboratory equipment such as vacuum ovens, freeze dryers, and vacuum desiccators.
– These pumps are crucial for applications like sample preparation, material testing, and scientific experiments requiring controlled environments.
4. Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing:
– The electronics and semiconductor industry heavily relies on piston vacuum pumps for various manufacturing processes.
– They are utilized in vacuum deposition systems for thin film coating, such as physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
– Piston pumps are also employed in vacuum furnaces for heat treatment processes in semiconductor fabrication.
– Other applications include vacuum packaging of electronic components and devices.
5. Food Processing and Packaging:
– Piston vacuum pumps play a significant role in the food processing and packaging industry.
– They are used for vacuum packaging of perishable food items, preventing spoilage and extending shelf life.
– In food processing, these pumps assist in vacuum concentration, freeze drying, and deaeration processes.
6. Environmental and Waste Management:
– Piston vacuum pumps find applications in environmental and waste management sectors.
– They are used in vacuum systems for wastewater treatment, including processes like aeration, filtration, and sludge dewatering.
– Piston pumps also assist in industrial and municipal waste management systems for vacuum collection or transfer of waste materials.
7. Other Industries:
– Piston vacuum pumps have diverse applications in additional industries:
– They are used in the glass manufacturing industry for vacuum lifting and handling of glass sheets or products.
– Piston pumps find application in the printing industry for vacuum feeding and ink transfer systems.
– They are employed in the power generation industry for steam condenser evacuation and turbine sealing systems.
In summary, piston vacuum pumps find widespread use in industries such as manufacturing and industrial processes, pharmaceuticals and medical, research and laboratory settings, electronics and semiconductor manufacturing, food processing and packaging, environmental and waste management, as well as in other sectors like glass manufacturing, printing, and power generation.

Are There Oil-Free Piston Vacuum Pump Options Available?
Yes, there are oil-free piston vacuum pump options available. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Oil-Free Technology:
– Traditional piston vacuum pumps use oil as a lubricant and sealant in their operation.
– However, advancements in vacuum pump technology have led to the development of oil-free piston vacuum pumps.
– Oil-free piston pumps are designed to operate without the need for lubricating oil, eliminating the risk of oil contamination and the need for oil changes.
2. Dry Running Operation:
– Oil-free piston vacuum pumps achieve lubrication and sealing through alternative means.
– They often utilize materials such as self-lubricating polymers or advanced coatings on the piston and cylinder surfaces.
– These materials reduce friction and provide sufficient sealing to maintain vacuum levels without the need for oil.
3. Applications:
– Oil-free piston vacuum pumps are suitable for a wide range of applications where oil contamination is a concern.
– They are commonly used in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceutical, electronics, laboratories, and medical where a clean and oil-free vacuum environment is required.
4. Advantages:
– The primary advantage of oil-free piston vacuum pumps is their ability to provide a clean and oil-free vacuum.
– They eliminate the risk of oil contamination, which is crucial in sensitive applications such as semiconductor manufacturing or pharmaceutical production.
– Oil-free pumps also simplify maintenance since there is no need for oil changes or regular oil monitoring.
5. Considerations:
– While oil-free piston vacuum pumps offer advantages, they also have some considerations to keep in mind.
– They may have slightly lower ultimate vacuum levels compared to oil-lubricated pumps.
– The absence of oil as a lubricant may result in slightly higher operating temperatures and increased wear on piston and cylinder surfaces.
– It’s important to select an oil-free piston vacuum pump that is suitable for the specific application requirements and consider the trade-offs between performance, cost, and maintenance.
6. Alternative Pump Technologies:
– In some cases, where oil-free operation is critical or specific vacuum levels are required, alternative pump technologies may be more suitable.
– Dry screw pumps, claw pumps, or scroll pumps are examples of oil-free pump technologies that are widely used in various industries.
– These pumps offer oil-free operation, high pumping speeds, and can achieve lower vacuum levels compared to oil-free piston pumps.
In summary, oil-free piston vacuum pumps are available as an alternative to traditional oil-lubricated pumps. They provide a clean and oil-free vacuum environment, making them suitable for applications where oil contamination is a concern. However, it’s important to consider specific application requirements and explore alternative pump technologies if necessary.


editor by CX 2024-03-30
China manufacturer Industrial Screw Piston AC Silent Oilless Oil Free Vacuum Low Noise Copper Home Small Highly Portable Rotary Part Mini Air Compressor Pump with high quality
Product Description
Scope of application:
Using for Pushing Pneumatic Nail Gun, Air Screw , Spray Painting Gun to work, also use to miniature instrument, blowing dust, Air inflation for small car and so on.
Product Feature:
- High Power, high efficiency, low energy, high reliability.
- Piston Ring: New ECO circle, low friction coefficient, Auto lubricating system.
- Cylinder Liner: Surface hardening, deplete hardness, Accelerate the heat transfer, long using time.
- Suction and exhaust valve: Using advanced foreign technology.
- Multiple Pressure: Overload protection
Oilless Air Compressor Featuers:
1.Super Silent
Super low noise.The output air pressure is stable without fluctuations, reducing noise pollution.
2. Safety
If the voltage or current cause the machine overheat, it will automatically shut down to protect from burnout.
3. Automatic control
Pressure switch automatically controls the start and stop of the machine.
4. Adjustable air pressure
The air pressure can be adjusted to meet the needs of different equipment usage.
5. Save human power
Switch on the air compressor can work normally & automatically. It is easy to operate and does not need human to be on duty.
6. Easy maintenance
No need to add any lubricant, easy maintenance after purchase.
Parts Features
1.Heavy cast iron body: heavy load, long stroke, low fuel consumption, low noise
2.Cylinder: made of high-grade cast iron, strength, good lubricity, wall by the fine honing, wear-resistant, durable
3.Piston ring: good elasticity, excellent wear resistance, low oil consumption, not easy to make the valve group carbon deposition and loss of oil to burn the crankshaft and connecting rod.
4.The crankshaft, connecting rod, piston: well balanced, wear resistance, high strength, smooth running balance.
5.High reliable and durable valve; strong aluminum alloy body, light and heat.
6.The motor provides reliable power, low voltage start up and running performance strong fan cooled motor and body; special shock proof design.
7.Double nozzles, were used to direct the exhaust and pressure exhaust; pressure switch with push button, safe and convenient
8.Oil free,silent,protect-environment,suitable for dental use.
Frequency Asked Question
1.Are you the manufacturer or trading company?
We are the manufacturer.
2.Where is your factory?
It is located in HangZhou City,ZHangZhoug Province,China.
3.What’s the terms of trade?
FOB,CFR,CIF or EXW are all acceptable.
4.What’s the terms of payment?
T/T,L/C at sight or cash.
5.What’s the lead time?
We are the manufacturer.
It is located in HangZhou City,ZHangZhoug Province,China.
FOB,CFR,CIF or EXW are all acceptable.
T/T,L/C at sight or cash.
In 15 days on receipt of deposit .
6.Do you accept sample order?
Yes,we accept.
7.What about the cost of sample?
You have to pay the freight charge.But the cost of product could be refundable,if you will purchase 1x20GP container in the future.
Yes,we accept.
You have to pay the freight charge.But the cost of product could be refundable,if you will purchase 1x20GP container in the future.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-less |
|---|---|
| Cooling System: | Air Cooling |
| Cylinder Arrangement: | Duplex Arrangement |
| Cylinder Position: | Vertical |
| Structure Type: | Open Type |
| Compress Level: | Double-Stage |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
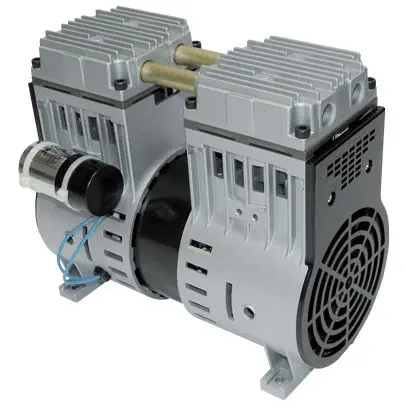

How Does a Piston Vacuum Pump Work?
A piston vacuum pump, also known as a reciprocating vacuum pump, operates using a piston mechanism to create a vacuum. Here’s a detailed explanation of its working principle:
1. Piston and Cylinder Assembly:
– A piston vacuum pump consists of a piston and cylinder assembly.
– The piston is a movable component that fits inside the cylinder and creates a seal between the piston and cylinder walls.
2. Intake and Exhaust Valves:
– The cylinder has two valves: an intake valve and an exhaust valve.
– The intake valve allows gas or air to enter the cylinder during the suction stroke, while the exhaust valve allows the expelled gas to exit during the compression stroke.
3. Suction Stroke:
– During the suction stroke, the piston moves downward, creating a vacuum within the cylinder.
– As the piston moves down, the intake valve opens, allowing gas or air from the system being evacuated to enter the cylinder.
– The volume within the cylinder increases, causing a decrease in pressure and the creation of a partial vacuum.
4. Compression Stroke:
– After the suction stroke, the piston moves upward during the compression stroke.
– As the piston moves up, the intake valve closes, preventing backflow of gas into the evacuated system.
– Simultaneously, the exhaust valve opens, allowing the gas trapped in the cylinder to be expelled.
– The upward movement of the piston reduces the volume within the cylinder, compressing the gas and increasing its pressure.
5. Expulsion of Gas:
– Once the compression stroke is complete, the gas is expelled through the exhaust valve.
– The exhaust valve then closes, ready for the next suction stroke.
– This process of alternating suction and compression strokes continues, gradually reducing the pressure within the evacuated system.
6. Lubrication:
– Piston vacuum pumps require lubrication for smooth operation and to maintain the airtight seal between the piston and cylinder walls.
– Lubricating oil is often introduced into the cylinder to provide lubrication and help maintain the seal.
– The oil also helps to cool the pump by dissipating heat generated during operation.
7. Applications:
– Piston vacuum pumps are commonly used in applications where high vacuum levels and low flow rates are required.
– They are suitable for processes such as laboratory work, vacuum drying, vacuum filtration, and other applications that require moderate vacuum levels.
In summary, a piston vacuum pump operates by creating a vacuum through the reciprocating motion of a piston within a cylinder. The suction stroke creates a vacuum by lowering the pressure within the cylinder, while the compression stroke expels the gas and increases its pressure. This cyclic process continues, gradually reducing the pressure within the system being evacuated. Piston vacuum pumps are commonly used in various applications that require moderate vacuum levels and low flow rates.
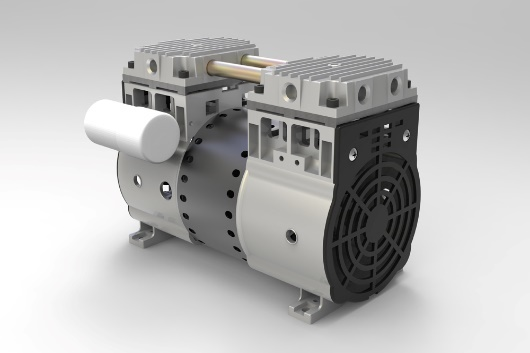
What Is the Energy Efficiency of Piston Vacuum Pumps?
The energy efficiency of piston vacuum pumps can vary depending on several factors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Design and Technology:
– The design and technology used in piston vacuum pumps can significantly influence their energy efficiency.
– Modern piston pump designs often incorporate features such as optimized valve systems, reduced internal leakage, and improved sealing mechanisms to enhance efficiency.
– Advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques have also contributed to more efficient piston pump designs.
2. Motor Efficiency:
– The motor driving the piston pump plays a crucial role in overall energy efficiency.
– High-efficiency motors, such as those adhering to energy efficiency standards like NEMA Premium or IE3, can significantly improve the energy efficiency of the pump.
– Proper motor sizing and matching to the pump’s load requirements are also important to maximize efficiency.
3. Control Systems:
– The use of advanced control systems can optimize the energy consumption of piston vacuum pumps.
– Variable frequency drives (VFDs) or speed control systems can adjust the pump’s operating speed based on the demand, reducing energy consumption during periods of lower demand.
– Smart control algorithms and sensors can also help optimize the pump’s performance and energy efficiency.
4. System Design and Integration:
– The overall system design and integration of the piston vacuum pump within the application can impact energy efficiency.
– Proper sizing and selection of the pump based on the specific application requirements can ensure that the pump operates within its optimal efficiency range.
– Efficient piping and ducting design, as well as minimizing pressure losses and leaks, can further improve the overall energy efficiency of the system.
5. Load Profile and Operating Conditions:
– The load profile and operating conditions of the piston vacuum pump have a significant impact on energy consumption.
– Higher vacuum levels or flow rates may require more energy to be supplied by the pump.
– Operating the pump continuously at maximum capacity may lead to higher energy consumption compared to intermittent or variable load conditions.
– It’s important to evaluate the specific operating requirements and adjust the pump’s operation accordingly to optimize energy efficiency.
6. Comparing Efficiency Ratings:
– When comparing the energy efficiency of different piston vacuum pumps, it can be helpful to look for efficiency ratings or specifications provided by the manufacturer.
– Some manufacturers provide efficiency data or performance curves indicating the pump’s energy consumption at various operating points.
– These ratings can assist in selecting a pump that meets the desired energy efficiency requirements.
In summary, the energy efficiency of piston vacuum pumps can be influenced by factors such as design and technology, motor efficiency, control systems, system design and integration, load profile, and operating conditions. Considering these factors and evaluating efficiency ratings can help in selecting an energy-efficient piston vacuum pump for a specific application.

What Is the Role of Lubrication in Piston Vacuum Pump Operation?
Lubrication plays a crucial role in the operation of a piston vacuum pump. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Reduction of Friction:
– Lubrication is essential for reducing friction between moving parts within the pump.
– In a piston vacuum pump, the piston moves up and down inside the cylinder, and lubrication helps to minimize the friction between the piston rings and the cylinder wall.
– By reducing friction, lubrication prevents excessive wear and heat generation, ensuring smooth and efficient operation of the pump.
2. Sealing and Leakage Prevention:
– Lubrication helps to maintain proper sealing between the piston rings and the cylinder wall.
– The lubricating oil forms a thin film between these surfaces, creating a barrier that prevents gas leakage during the compression and vacuum creation process.
– Effective sealing is crucial for maintaining the desired vacuum level and preventing air or gas from entering the pump.
3. Cooling and Heat Dissipation:
– Piston vacuum pumps generate heat during operation, particularly due to the compression of gases.
– Lubricating oil helps in dissipating the heat generated, preventing the pump from overheating.
– The oil absorbs heat from the pump’s internal components and transfers it to the pump’s housing or cooling system.
– Proper cooling and heat dissipation contribute to the pump’s overall performance and prevent damage due to excessive heat buildup.
4. Contaminant Removal:
– Lubrication also aids in removing contaminants or particles that may enter the pump.
– The oil acts as a carrier, trapping and carrying away small particles or debris that could potentially damage the pump’s components.
– The oil passes through filters that help to remove these contaminants, keeping the pump’s internal parts clean and functioning properly.
5. Corrosion Prevention:
– Some lubricating oils contain additives that provide corrosion protection.
– These additives form a protective film on the pump’s internal surfaces, preventing corrosion caused by exposure to moisture or corrosive gases.
– Corrosion prevention is crucial for maintaining the pump’s performance, extending its lifespan, and minimizing the need for repairs or component replacement.
6. Proper Lubrication Selection:
– Selecting the appropriate lubricating oil is essential for the proper functioning of a piston vacuum pump.
– Different pump models and manufacturers may recommend specific oil types or viscosities to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
– It is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding oil selection, oil level, and oil change intervals.
In summary, lubrication plays a vital role in piston vacuum pump operation by reducing friction, maintaining proper sealing, dissipating heat, removing contaminants, and preventing corrosion. Proper lubrication selection and adherence to manufacturer’s guidelines are crucial for ensuring the pump’s efficient and reliable performance.


editor by CX 2024-03-23
China Hot selling Whc Solar Pump for Deep Well Rotary Piston Vacuum Pump Water Cooling Pump vacuum pump engine
Product Description
WHC SOLAR System Solar Pump Inverter Solar Power 60-90V DC Water Pump Solar Surface Water Pump
Model: WHC550-48-24-6PM
Product Name: Solar Surface PM Water Pump System
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
| Overview | |
| Product Name | Solar Surface PM Water Pump System |
| Model | WHC550-48-24-6PM |
| Max Head | 24m |
| Rate Head | 16m |
| Max Flow Rate | 6000L/H |
| Rated Flow Rate | 4000L/H |
| Specifications | |
| Solar Panel | High Efficiency Mono 120W*8PCS |
| Motor power | 550W |
| Mppt Controller | 48V15A |
| Woking Time | Daytime |
| Application | River,Lake,Pool,Irrigation,Home |
| Outlet Inch | 1″ |
| Speed of motor | 2850r/min |
| Material of pump | Steel |
PRODUCT FEATURES
| Related Information | |
| CBM/Set | 0.25 |
| Weight(kg)/Set | 81 |
| Solar Input (Voc) | <100V |
| Solar Input Range (Vmp) | 60-90V |
| Theory | Centrifugal Pump |
| Impeller | Plastic-steel ,Scerw |
| Working principle | DC Brushless |
| Feature | High Efficiency;Long life |
| Pressure | High Pressure |
| Controller Protection Class | IP65 |
SYSTEM APPLICATIONS
TECHNICAL PARAMETERS
HOT SALE PRODUCTS
COMPANY PROFILE
FACTORY STRENGTH
CERTIFICATE DISPLAY
PACKING & DELIVERY
FAQ
Q1. MOQ& Samples.
A: MOQ is 1 PC. Welcome sample order to test and check quality. Customized is available.
Q2. What about the lead time?
A: Samples within 10 days, big order within 4 weeks.
Q3. How do you ship the goods?
A: By sea. We have MSDS,test report for safe transport and non-dangerous products.
Q4. Is it OK to print my logo on product?
A: Yes. Free logo print.
Q5. Do you offer guarantee for the products?
A: Yes. We offer 1-3 years’ warranty to our products. The time depends on the goods model.
Q6. How to deal with the faulty?
A: Firstly, our products are produced in strict quality control system and the defective rate will be less than 0.01%.Secondly, during the warranty period, we will repair or replace defected products.
Q7. Are you manufacturer or trading company?
A: Manufacturer. Factory is located in ZheJiang province. Show room is located in HangZhou.
Q8. If we could accept OEM &ODM Service?
Accept customized, such as the brand, Logo, Container color etc.
Thank you for your read!
Website:whc-solar.en.Made-in-China.com
If you have any doubt please no hesitate to contact me, we are sure any your question will get our prompt reply.
We look CZPT to establish business relationship with you!
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Yes |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 3 Years |
| Condition: | New |
| Certification: | ISO, CE, RoHS |
| Application: | Home, Industrial, Commercial, Outdoor |
| Specification: | Normal, 550W 48V 24M 6PM |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What Are the Key Components of a Piston Vacuum Pump?
A piston vacuum pump consists of several key components that work together to create a vacuum. Here’s a detailed explanation of these components:
1. Cylinder:
– The cylinder is a cylindrical chamber where the piston moves back and forth.
– It provides the housing for the piston and plays a crucial role in creating the vacuum by changing the volume of the chamber.
2. Piston:
– The piston is a movable component that fits inside the cylinder.
– It creates a seal between the piston and cylinder walls, allowing the pump to create a pressure differential and generate a vacuum.
– The piston is typically driven by a motor or an external power source.
3. Intake Valve:
– The intake valve allows gas or air to enter the cylinder during the suction stroke.
– It opens when the piston moves downward, creating a vacuum and drawing gas into the cylinder from the system being evacuated.
4. Exhaust Valve:
– The exhaust valve allows the expelled gas to exit the cylinder during the compression stroke.
– It opens when the piston moves upward, allowing the compressed gas to be expelled from the cylinder.
5. Lubrication System:
– Piston vacuum pumps often incorporate a lubrication system to ensure smooth operation and maintain an airtight seal between the piston and cylinder walls.
– Lubricating oil is introduced into the cylinder to provide lubrication and help maintain the seal.
– The lubrication system also helps to cool the pump by dissipating heat generated during operation.
6. Cooling System:
– Some piston vacuum pumps may include a cooling system to prevent overheating.
– This can involve the circulation of a cooling fluid or the use of cooling fins to dissipate heat generated during operation.
7. Pressure Gauges and Controls:
– Pressure gauges are often installed to monitor the vacuum level or pressure within the system.
– Control mechanisms, such as switches or valves, may be present to regulate the operation of the pump or maintain the desired vacuum level.
8. Motor or Power Source:
– The piston in a piston vacuum pump is typically driven by a motor or an external power source.
– The motor provides the necessary mechanical energy to move the piston back and forth, creating the suction and compression strokes.
9. Frame or Housing:
– The components of the piston vacuum pump are housed within a frame or housing that provides structural support and protection.
– The frame or housing also helps to reduce noise and vibration during operation.
In summary, the key components of a piston vacuum pump include the cylinder, piston, intake valve, exhaust valve, lubrication system, cooling system, pressure gauges and controls, motor or power source, and the frame or housing. These components work together to create a vacuum by reciprocating the piston within the cylinder, allowing gas to be drawn in and expelled, while maintaining an airtight seal. The lubrication and cooling systems, as well as pressure gauges and controls, ensure smooth and efficient operation of the pump.

Can Piston Vacuum Pumps Be Used in Medical or Pharmaceutical Applications?
Yes, piston vacuum pumps can be used in medical and pharmaceutical applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
– Piston vacuum pumps are versatile and widely used in various industries, including medical and pharmaceutical sectors.
– Medical and pharmaceutical applications often require vacuum technology for processes such as filtration, degassing, drying, and sample preparation.
– Piston vacuum pumps offer several advantages that make them suitable for these applications:
– High Vacuum Levels: Piston pumps can achieve high vacuum levels, which are often necessary in medical and pharmaceutical processes that require precise control and removal of gases or vapors.
– Contamination-Free Operation: Piston pumps can provide contamination-free operation, making them suitable for applications where maintaining a sterile or clean environment is crucial, such as in pharmaceutical manufacturing or medical research laboratories.
– Oil-Free Operation: Some piston vacuum pumps are designed to operate without oil lubrication. Oil-free pumps eliminate the risk of oil contamination in sensitive medical or pharmaceutical processes and avoid the need for oil changes or maintenance associated with oil-lubricated pumps.
– Quiet Operation: Piston pumps can be engineered to operate with reduced noise levels, which is advantageous in medical and pharmaceutical settings where a quiet working environment is desired.
– Durability and Reliability: Piston pumps are known for their robust construction and durability, allowing them to withstand demanding applications and provide reliable performance over extended periods.
– Compact Size: Piston vacuum pumps are available in compact designs, making them suitable for applications where space is limited, such as in medical devices or portable pharmaceutical equipment.
– Some specific medical and pharmaceutical applications where piston vacuum pumps are commonly used include:
– Vacuum Filtration: Piston pumps are used to generate the necessary vacuum for filtering solutions or suspensions in laboratory or industrial settings. This process is often employed in pharmaceutical research, production of vaccines, or purification of drugs.
– Freeze Drying: Piston vacuum pumps assist in the freeze-drying process, which is a common technique used in the pharmaceutical industry to preserve and stabilize sensitive drugs or biological samples.
– Vacuum Packaging: Piston pumps are utilized for creating a vacuum in packaging processes where maintaining product quality and extending shelf life are critical, such as in the pharmaceutical packaging of medicines or medical devices.
– Laboratory Evaporation: Piston vacuum pumps are employed in laboratory applications for the evaporation of solvents or liquids in medical or pharmaceutical research, drug development, or quality control processes.
– It is important to select the appropriate piston vacuum pump model based on the specific requirements of the medical or pharmaceutical application. Factors to consider include vacuum level needed, flow rate, compatibility with the handled substances, and compliance with industry regulations and standards.
– Additionally, compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other regulatory guidelines is crucial when using piston vacuum pumps in medical or pharmaceutical applications to ensure product safety, quality, and regulatory compliance.
In summary, piston vacuum pumps are suitable for use in medical and pharmaceutical applications due to their ability to achieve high vacuum levels, provide contamination-free and oil-free operation, offer quiet and reliable performance, and accommodate compact design requirements. They are commonly used in processes such as vacuum filtration, freeze drying, vacuum packaging, and laboratory evaporation in these industries.

Are There Oil-Free Piston Vacuum Pump Options Available?
Yes, there are oil-free piston vacuum pump options available. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Oil-Free Technology:
– Traditional piston vacuum pumps use oil as a lubricant and sealant in their operation.
– However, advancements in vacuum pump technology have led to the development of oil-free piston vacuum pumps.
– Oil-free piston pumps are designed to operate without the need for lubricating oil, eliminating the risk of oil contamination and the need for oil changes.
2. Dry Running Operation:
– Oil-free piston vacuum pumps achieve lubrication and sealing through alternative means.
– They often utilize materials such as self-lubricating polymers or advanced coatings on the piston and cylinder surfaces.
– These materials reduce friction and provide sufficient sealing to maintain vacuum levels without the need for oil.
3. Applications:
– Oil-free piston vacuum pumps are suitable for a wide range of applications where oil contamination is a concern.
– They are commonly used in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceutical, electronics, laboratories, and medical where a clean and oil-free vacuum environment is required.
4. Advantages:
– The primary advantage of oil-free piston vacuum pumps is their ability to provide a clean and oil-free vacuum.
– They eliminate the risk of oil contamination, which is crucial in sensitive applications such as semiconductor manufacturing or pharmaceutical production.
– Oil-free pumps also simplify maintenance since there is no need for oil changes or regular oil monitoring.
5. Considerations:
– While oil-free piston vacuum pumps offer advantages, they also have some considerations to keep in mind.
– They may have slightly lower ultimate vacuum levels compared to oil-lubricated pumps.
– The absence of oil as a lubricant may result in slightly higher operating temperatures and increased wear on piston and cylinder surfaces.
– It’s important to select an oil-free piston vacuum pump that is suitable for the specific application requirements and consider the trade-offs between performance, cost, and maintenance.
6. Alternative Pump Technologies:
– In some cases, where oil-free operation is critical or specific vacuum levels are required, alternative pump technologies may be more suitable.
– Dry screw pumps, claw pumps, or scroll pumps are examples of oil-free pump technologies that are widely used in various industries.
– These pumps offer oil-free operation, high pumping speeds, and can achieve lower vacuum levels compared to oil-free piston pumps.
In summary, oil-free piston vacuum pumps are available as an alternative to traditional oil-lubricated pumps. They provide a clean and oil-free vacuum environment, making them suitable for applications where oil contamination is a concern. However, it’s important to consider specific application requirements and explore alternative pump technologies if necessary.


editor by CX 2023-12-17
China best Water Ring Vacuum Pump Air Rotary Oil Water Piston Dry Portable Mini Scroll Reciprocating Diaphragm Centrifugal Positive Displacement DC AC Vacuum Pumps vacuum pump adapter
Product Description
Water Ring Vacuum Pump Air Rotary Oil Water Piston Dry Portable Mini Scroll Reciprocating Diaphragm Centrifugal Positive Displacement DC AC Vacuum Pumps
water vacuum pump
Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump Working Principle. The vacuum pump consisting an impeller which is located eccentric to the cylinder body(Vacuum pump housing). Vacuum is created in the vacuum pump by using a liquid seal. … When the impeller starts to rotate, the liquid is starts move outward by centrifugal force.
Water ring vacuum pump is a common type of liquid ring vacuum pump. Water ring is a rotor with multi-blades eccentrically installed in the pump shell. When it rotates, it throws liquid into the pump and forms a liquid ring concentric with the pump shell. The liquid ring and the rotor blade form a rotating variable capacity vacuum pump with periodic volume change. When the working liquid is water, it is called water Ring vacuum pump. There are many kinds of water ring vacuum pumps with different prices. .Among them, 2BV is more cost-effective. The type selection of water ring vacuum pump should be based on your on-site process, the required vacuum degree and the amount of air pumping required.
company information
| After-sales Service: | Installation Guide 1-Year Warranty |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | Installation Guide 1-Year Warranty |
| Oil or Not: | Optional |
| Structure: | – |
| Exhauster Method: | – |
| Vacuum Degree: | – |
| Samples: |
US$ 999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

Can Piston Vacuum Pumps Create a Deep Vacuum?
Yes, piston vacuum pumps have the capability to create a deep vacuum. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Piston vacuum pumps are designed to generate and maintain a vacuum by using a reciprocating piston mechanism. They can achieve vacuum levels ranging from millitorr (10-3 Torr) to microns (10-6 Torr), which is considered a deep vacuum range.
When the piston moves downward during the suction stroke, it creates a vacuum within the cylinder. This allows gas or air from the system being evacuated to enter the cylinder. As the piston moves up during the compression stroke, the gas is expelled from the cylinder, reducing its volume and increasing its pressure. This cyclic process continues, gradually reducing the pressure within the system.
One of the factors that contribute to the ability of piston vacuum pumps to create a deep vacuum is the use of an airtight seal between the piston and cylinder walls. This seal prevents the gas from leaking back into the evacuated system, allowing the pump to maintain the desired vacuum level.
It’s important to note that the achievable vacuum level of a piston vacuum pump can depend on various factors, including the design of the pump, the materials used, the quality of the seals, and the operating conditions. Additionally, the flow rate of the pump may be lower compared to other types of vacuum pumps, as piston pumps are typically designed for applications that require low flow rates but high vacuum levels.
In summary, piston vacuum pumps can create a deep vacuum in the millitorr to micron range. With their reciprocating piston mechanism and airtight seals, they are capable of generating and maintaining a vacuum suitable for applications that require deep vacuum conditions.

Are There Noise Considerations When Using Piston Vacuum Pumps?
Yes, there are noise considerations to take into account when using piston vacuum pumps. Here’s a detailed explanation:
– Piston vacuum pumps can generate noise during their operation, which is important to consider, especially in environments where noise levels need to be minimized.
– The noise produced by piston vacuum pumps is primarily caused by mechanical vibrations and the movement of internal components.
– The noise level can vary depending on factors such as the design and construction of the pump, the speed of operation, and the load conditions.
– Excessive noise from piston vacuum pumps can have several implications:
– Occupational Health and Safety: High noise levels can pose a risk to the health and safety of operators and personnel working in the vicinity of the pump. Prolonged exposure to loud noise can lead to hearing damage and other related health issues.
– Environmental Impact: In certain settings, such as residential areas or noise-sensitive locations, excessive noise from piston vacuum pumps may result in noise pollution and non-compliance with local noise regulations.
– Equipment Interference: Noise generated by the pump can interfere with the operation of nearby sensitive equipment, such as electronic devices or precision instruments, potentially affecting their performance.
– To mitigate the noise produced by piston vacuum pumps, several measures can be taken:
– Enclosures and Sound Insulation: Installing acoustic enclosures or sound-insulating materials around the pump can help contain and reduce the noise. These enclosures are designed to absorb or block the sound waves generated by the pump.
– Vibration Isolation: Using vibration isolation mounts or pads can help minimize the transmission of vibrations from the pump to surrounding structures, reducing the noise level.
– Maintenance and Lubrication: Regular maintenance, including lubrication of moving parts, can help reduce friction and mechanical noise generated by the pump.
– Operating Conditions: Adjusting the operating conditions of the pump, such as speed and load, within the manufacturer’s specified limits can help optimize performance and minimize noise generation.
– Location and Placement: Proper positioning and placement of the pump, considering factors such as distance from occupied areas or sensitive equipment, can help minimize the impact of noise.
– It is important to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations regarding noise levels and any specific measures to mitigate noise for a particular piston vacuum pump model.
– Compliance with local regulations and standards regarding noise emissions should also be considered and adhered to.
In summary, noise considerations are important when using piston vacuum pumps to ensure the health and safety of personnel, minimize environmental impact, and prevent interference with other equipment. Measures such as enclosures, vibration isolation, maintenance, and proper operating conditions can help mitigate the noise generated by these pumps.
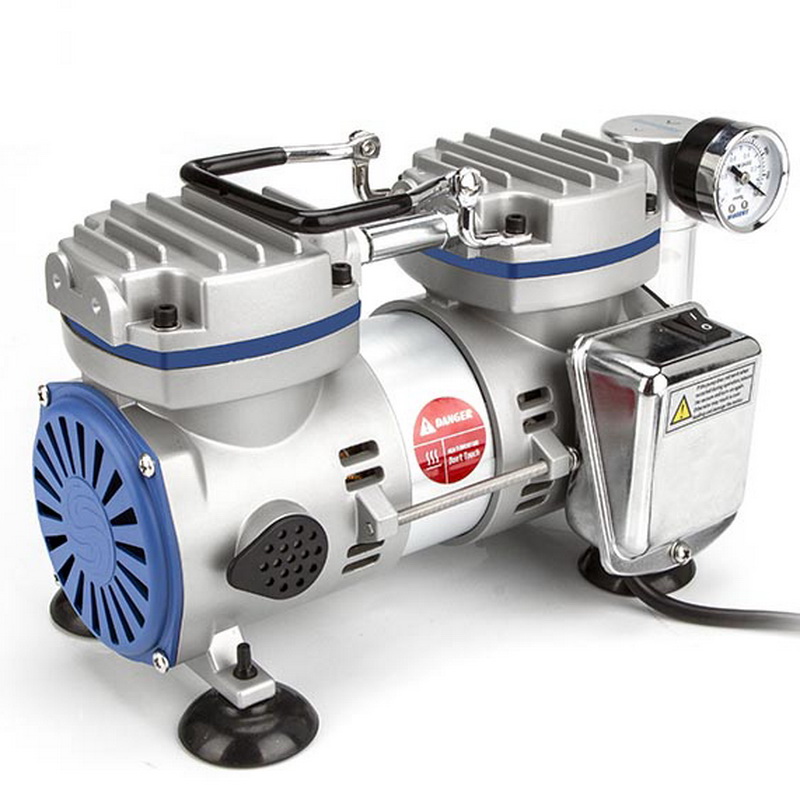

How Do You Maintain and Service a Piston Vacuum Pump?
Maintaining and servicing a piston vacuum pump is essential to ensure its optimal performance and longevity. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Regular Inspection:
– Perform regular visual inspections of the pump to check for any signs of damage, leaks, or wear.
– Inspect the seals, gaskets, and fittings for any cracks or deterioration.
– Ensure that all connections are tight and secure.
2. Oil Change:
– Piston vacuum pumps typically require regular oil changes to maintain proper lubrication and prevent contamination.
– Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding the frequency of oil changes.
– Drain the old oil completely and replace it with the recommended oil type and quantity.
– Dispose of the used oil according to proper environmental regulations.
3. Filter Replacement:
– Many piston vacuum pumps have filters to prevent dust, particles, and contaminants from entering the pump.
– Check the filter regularly and replace it as needed to maintain proper airflow and prevent clogging.
4. Cleaning:
– Keep the exterior of the pump and its surrounding area clean and free from debris.
– Use a soft cloth or brush to remove any dust or dirt accumulation.
– Avoid using harsh chemicals or solvents that may damage the pump’s surfaces.
5. Seals and Gaskets:
– Inspect the seals and gaskets regularly and replace them if they show signs of wear or damage.
– Ensure that the seals provide a proper airtight seal to prevent leaks and maintain vacuum performance.
6. Cooling System:
– If the piston vacuum pump has a cooling system, monitor it regularly to ensure proper functioning.
– Clean or replace the cooling system components as recommended by the manufacturer.
7. Professional Maintenance:
– Consider scheduling professional maintenance and service at regular intervals, especially for more complex or critical applications.
– Professional technicians can perform in-depth inspections, conduct performance tests, and address any specific issues or concerns.
– They can also provide recommendations on optimizing the pump’s performance and extending its lifespan.
8. Manufacturer Guidelines:
– Always refer to the manufacturer’s maintenance and service guidelines specific to your piston vacuum pump model.
– Follow their recommendations regarding oil type, oil level, maintenance intervals, and any other specific instructions.
– Adhering to the manufacturer’s guidelines ensures proper operation and prevents voiding the warranty.
In summary, maintaining and servicing a piston vacuum pump involves regular inspection, oil changes, filter replacement, cleaning, checking seals and gaskets, monitoring the cooling system, and considering professional maintenance. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines is crucial for effective maintenance and to maximize the pump’s performance and lifespan.


editor by CX 2023-12-11
China Standard Water Vacuum Pump Air Rotary Ring Oil Water Piston Dry Portable Mini Scroll Reciprocating Diaphragm Centrifugal Positive Displacement DC AC Vacuum Pump a/c vacuum pump
Product Description
Water Vacuum Pump Air Rotary Ring Oil Water Piston Dry Portable Mini Scroll Reciprocating Diaphragm Centrifugal Positive Displacement DC AC Vacuum Pump
water vacuum pump
Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump Working Principle. The vacuum pump consisting an impeller which is located eccentric to the cylinder body(Vacuum pump housing). Vacuum is created in the vacuum pump by using a liquid seal. … When the impeller starts to rotate, the liquid is starts move outward by centrifugal force.
Water ring vacuum pump is a common type of liquid ring vacuum pump. Water ring is a rotor with multi-blades eccentrically installed in the pump shell. When it rotates, it throws liquid into the pump and forms a liquid ring concentric with the pump shell. The liquid ring and the rotor blade form a rotating variable capacity vacuum pump with periodic volume change. When the working liquid is water, it is called water Ring vacuum pump. There are many kinds of water ring vacuum pumps with different prices. .Among them, 2BV is more cost-effective. The type selection of water ring vacuum pump should be based on your on-site process, the required vacuum degree and the amount of air pumping required.
company information
| After-sales Service: | Installation Guide 1-Year Warranty |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | Installation Guide 1-Year Warranty |
| Oil or Not: | Optional |
| Inlet Diam. (mm): | 100/200mm |
| Motor Power (Kw): | 4/7.5 Kw |
| Ultimate Pressure (PA): | 0.05 |
| Samples: |
US$ 999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

What Are the Typical Applications of Piston Vacuum Pumps?
Piston vacuum pumps find applications in various industries and processes. Here’s a detailed explanation of the typical applications of piston vacuum pumps:
1. Laboratories and Research Facilities:
– Piston vacuum pumps are commonly used in laboratories and research facilities for a wide range of applications.
– They are utilized in vacuum ovens, freeze dryers, vacuum filtration systems, and other equipment requiring controlled evacuation.
2. Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology:
– In the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, piston vacuum pumps are employed for processes such as solvent evaporation, distillation, and filtration.
– They are used in drug manufacturing, vaccine production, and research involving biochemistry and molecular biology.
3. Food Processing and Packaging:
– Piston vacuum pumps play a vital role in the food processing and packaging industry.
– They are used in vacuum packaging machines to remove air from packaging containers, extending the shelf life of food products.
4. HVAC and Refrigeration Systems:
– Piston vacuum pumps are utilized in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems and refrigeration systems.
– They help evacuate air and moisture from the systems to achieve the desired pressure and prevent contamination.
5. Manufacturing and Industrial Processes:
– Piston vacuum pumps are employed in various manufacturing and industrial processes.
– They are used for degassing, vacuum impregnation, vacuum drying, and other applications that require controlled evacuation.
6. Automotive Industry:
– In the automotive industry, piston vacuum pumps are often used in brake booster systems.
– They create a vacuum to assist in brake actuation, providing the necessary power for braking.
7. Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing:
– Piston vacuum pumps are utilized in electronics and semiconductor manufacturing processes.
– They help create a controlled environment with low-pressure conditions during the production of microchips, integrated circuits, and other electronic components.
8. Environmental Monitoring and Analysis:
– Piston vacuum pumps are utilized in environmental monitoring and analysis equipment.
– They are used in air sampling devices, gas analyzers, and other instruments that require precise vacuum control.
9. Scientific Research and Vacuum Systems:
– Piston vacuum pumps are employed in various scientific research applications.
– They are used in vacuum systems for particle accelerators, electron microscopes, mass spectrometers, surface analysis instruments, and other scientific equipment.
In summary, piston vacuum pumps have diverse applications in laboratories, pharmaceuticals, food processing, HVAC systems, manufacturing processes, automotive industry, electronics, environmental monitoring, scientific research, and more. Their ability to provide controlled evacuation and achieve moderate vacuum levels makes them suitable for a wide range of industries and processes.

What Industries Commonly Rely on Piston Vacuum Pumps?
Various industries rely on piston vacuum pumps for their specific applications and requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Manufacturing and Industrial Processes:
– Piston vacuum pumps find extensive use in manufacturing and industrial processes across different sectors.
– They are commonly employed in vacuum packaging, where they help create a vacuum environment to preserve and extend the shelf life of food products.
– In the automotive industry, piston vacuum pumps are utilized in brake booster systems to provide the necessary vacuum for power braking.
– Other industrial applications include vacuum molding, vacuum drying, vacuum distillation, and vacuum filtration.
2. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Industry:
– The pharmaceutical and medical industry extensively relies on piston vacuum pumps for various critical processes.
– These pumps are used in pharmaceutical manufacturing for vacuum drying, solvent recovery, and distillation processes.
– In medical applications, piston vacuum pumps are utilized in vacuum suction devices and medical laboratory equipment.
– They are also employed in vacuum autoclaves for sterilization purposes.
3. Research and Laboratory Settings:
– Piston vacuum pumps are commonly found in research laboratories and scientific facilities.
– They are used for creating vacuum conditions in laboratory equipment such as vacuum ovens, freeze dryers, and vacuum desiccators.
– These pumps are crucial for applications like sample preparation, material testing, and scientific experiments requiring controlled environments.
4. Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing:
– The electronics and semiconductor industry heavily relies on piston vacuum pumps for various manufacturing processes.
– They are utilized in vacuum deposition systems for thin film coating, such as physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
– Piston pumps are also employed in vacuum furnaces for heat treatment processes in semiconductor fabrication.
– Other applications include vacuum packaging of electronic components and devices.
5. Food Processing and Packaging:
– Piston vacuum pumps play a significant role in the food processing and packaging industry.
– They are used for vacuum packaging of perishable food items, preventing spoilage and extending shelf life.
– In food processing, these pumps assist in vacuum concentration, freeze drying, and deaeration processes.
6. Environmental and Waste Management:
– Piston vacuum pumps find applications in environmental and waste management sectors.
– They are used in vacuum systems for wastewater treatment, including processes like aeration, filtration, and sludge dewatering.
– Piston pumps also assist in industrial and municipal waste management systems for vacuum collection or transfer of waste materials.
7. Other Industries:
– Piston vacuum pumps have diverse applications in additional industries:
– They are used in the glass manufacturing industry for vacuum lifting and handling of glass sheets or products.
– Piston pumps find application in the printing industry for vacuum feeding and ink transfer systems.
– They are employed in the power generation industry for steam condenser evacuation and turbine sealing systems.
In summary, piston vacuum pumps find widespread use in industries such as manufacturing and industrial processes, pharmaceuticals and medical, research and laboratory settings, electronics and semiconductor manufacturing, food processing and packaging, environmental and waste management, as well as in other sectors like glass manufacturing, printing, and power generation.

Can Piston Vacuum Pumps Handle Corrosive Gases or Vapors?
Piston vacuum pumps are generally not suitable for handling corrosive gases or vapors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Construction Materials:
– Piston vacuum pumps are typically constructed with materials such as cast iron, aluminum, stainless steel, and various elastomers.
– While these materials offer good resistance to normal operating conditions, they may not be compatible with corrosive substances.
– Corrosive gases or vapors can attack and degrade the pump’s internal components, leading to reduced performance, increased wear, and potential failure.
2. Sealing and Contamination:
– Piston vacuum pumps rely on tight seals and clearances to maintain the vacuum and prevent leakage.
– Corrosive gases or vapors can degrade the seals and compromise their effectiveness.
– This can result in increased leakage, reduced pumping efficiency, and potential contamination of the pump and the surrounding environment.
3. Maintenance and Service:
– Handling corrosive gases or vapors requires specialized knowledge, materials, and maintenance procedures.
– The pump may need additional protective measures, such as corrosion-resistant coatings or specialized seal materials, to withstand the corrosive environment.
– Regular inspection, cleaning, and replacement of components may also be necessary to maintain the pump’s performance and prevent damage.
4. Alternative Pump Options:
– If corrosive gases or vapors are involved in the application, it is advisable to consider alternative pump technologies that are specifically designed to handle such substances.
– For corrosive gases, chemical-resistant pumps like diaphragm pumps, peristaltic pumps, or dry screw pumps may be more suitable.
– These pumps are constructed with materials that offer superior resistance to corrosion and can handle a wide range of corrosive substances.
– It is essential to consult the pump manufacturer or a vacuum system specialist to select the appropriate pump for handling corrosive gases or vapors.
In summary, piston vacuum pumps are generally not recommended for handling corrosive gases or vapors due to their construction materials, sealing limitations, and the potential for damage and contamination. It is crucial to choose a pump specifically designed to handle corrosive substances or consider alternative pump technologies that can provide the required chemical resistance and performance.


editor by CX 2023-12-06