Product Description
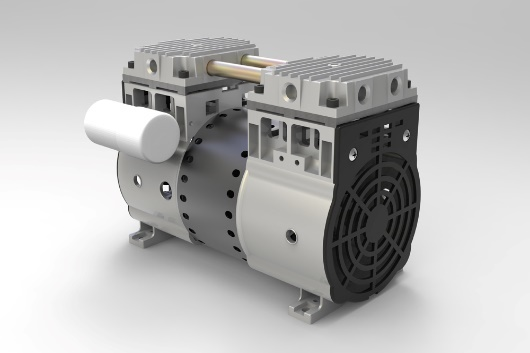
Pransch PM1400V High Quality Portable Oil Free oilless dry Air Compressor Dental Vacuum Pump
Advantages:
Oil-less Vacuum Pumps / Air Compressors
PRANSCH oil-less rocking piston pump and air compressor combines the best characteristics of traditional piston pumps(air compressor) and diaphragm pumps into small units with excellent features.
- Light weight and very portable
- Durable and near ZERO maintenance
- Thermal protection (130 deg C)
- Power cord with plug, 1m length
- Shock mount
- Silencer – muffler
- Stainless steel vacuum and pressure gauge, both with oil damping
- Two stainless steel needle valves each with lock nut.
- All nickel plated fittings
- Power supply 230V, 50/60 Hz
Main application fields:
machines for pressotherapy, machines for dermabrasion, inhalation thermal therapies, money counting machines, silk screen printing machines, automatic feeder machines for book-binding, wood presses, suction lifting machines, pollutant sampling and analysis.
Specification:
| Model | Frequency | Flow | Pressure | Power | Speed | Current | Voltage | Heat | Sound | Weight | Hole | Installation Dimensions |
| Hz | L/min | Kpa | Kw | Min-1 | A | V | 0 C | db(A) | Kg | MM | MM | |
| PM200V | 50 | 33 | -84 | 0.10 | 1380 | 0.45 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 48 | 1.8 | 5 | L100xW74 |
| 60 | 50 | -84 | 0.12 | 1450 | 0.90 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 48 | 1.8 | 5 | ||
| PM300V | 50 | 66 | -86 | 0.12 | 1380 | 0.56 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 50 | 3.2 | 6 | L118xW70 |
| 60 | 75 | -86 | 0.14 | 1450 | 1.13 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 50 | 3.2 | 6 | ||
| PM400V | 50 | 80 | -92 | 0.32 | 1380 | 0.95 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 56 | 6.0 | 6 | L153xW95 |
| 60 | 92 | -92 | 0.36 | 1450 | 1.91 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 56 | 6.0 | 6 | ||
| PM550V | 50 | 100 | -92 | 0.32 | 1380 | 1.50 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 56 | 6.0 | 6 | L148xW83 |
| 60 | 110 | -92 | 0.36 | 1450 | 3.10 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 56 | 6.0 | 6 | ||
| PM1400V | 50 | 166 | -92 | 0.45 | 1380 | 1.90 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 58 | 8.5 | 6 | L203xW86 |
| 60 | 183 | -92 | 0.52 | 1450 | 4.10 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 58 | 8.5 | 6 | ||
| PM2000V | 50 | 216 | -92 | 0.55 | 1380 | 2.50 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 60 | 9.0 | 6 | L203xW86 |
| 60 | 250 | -92 | 0.63 | 1450 | 5.20 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 60 | 9.0 | 6 | ||
| HP2400V | 50 | 225 | -94 | 0.90 | 1380 | 3.30 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 75 | 17.0 | 7 | L246xW127 |
| 60 | 258 | -94 | 1.10 | 1450 | 6.90 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 75 | 17.0 | 7 | ||
| PM3000V | 50 | 230 | -94 | 1.10 | 1380 | 4.20 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 76 | 17.5 | 7 | L246xW127 |
| 60 | 266 | -94 | 1.30 | 1450 | 8.50 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 76 | 17.5 | 7 |
Why use a Rocking Piston Product?
Variety
Pransch oilless Rocking Piston air compressors and vacuum pumps, available in single, twin, miniature, and tankmounted
styles, are the perfect choice for hundreds of applications. Choose from dual frequency, shaded pole,
and permanent split capacitor (psc) electric motors with AC multi-voltage motors to match North American,
European, and CZPT power supplies. A complete line of recommended accessories as well as 6, 12, and
24 volt DC models in brush and brushless types are also available.
Performance
The rocking piston combines the best characteristics of piston and diaphragm air compressors into a small unit
with exceptional performance. Air flow capabilities from 3.4 LPM to 5.5 CFM (9.35 m3/h), pressure to 175 psi
(12.0 bar) and vacuum capabilities up to 29 inHg (31 mbar). Horsepowers range from 1/20 to 1/2 HP
(0.04 to 0.37 kW).
Reliable
These pumps are made to stand up through years of use. The piston rod and bearing assembly are bonded
together, not clamped; they will not slip, loosen, or misalign to cause trouble.
Clean Air
Because CZPT pumps are oil-free, they are ideal for use in applications in laboratories, hospitals, and the
food industry where oil mist contamination is undesirable.
Application:
- Transportation application include:Auto detailing Equipment,Braking Systems,Suspension Systems,Tire Inflators
- Food and Beverage application include:beverage dispensing,coffee and Espresso equipment,Food processing and packaging,Nitrogen Generation
- Medical and laboratory application include:Body fluid Analysis equipment,Dental compressors and hand tools,dental vacuum ovens,Dermatology equipment,eye surgery equipment,lab automation,Liposuction equipment,Medical aspiration,Nitrogen Generation,Oxygen concentrators,Vacuum Centrifuge,vacuum filtering,ventilators
- General industrial application include:Cable pressurization,core drilling
- Environmental application include:Dry sprinkler systems,Pond Aeration,Refrigerant Reclamation,Water Purification Systems
- Printing and packaging application include:vacuum frames
- material Handling application include:vacuum mixing
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Reciprocating Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Positive Displacement Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | High Vacuum |
| Work Function: | Mainsuction Pump |
| Working Conditions: | Dry |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
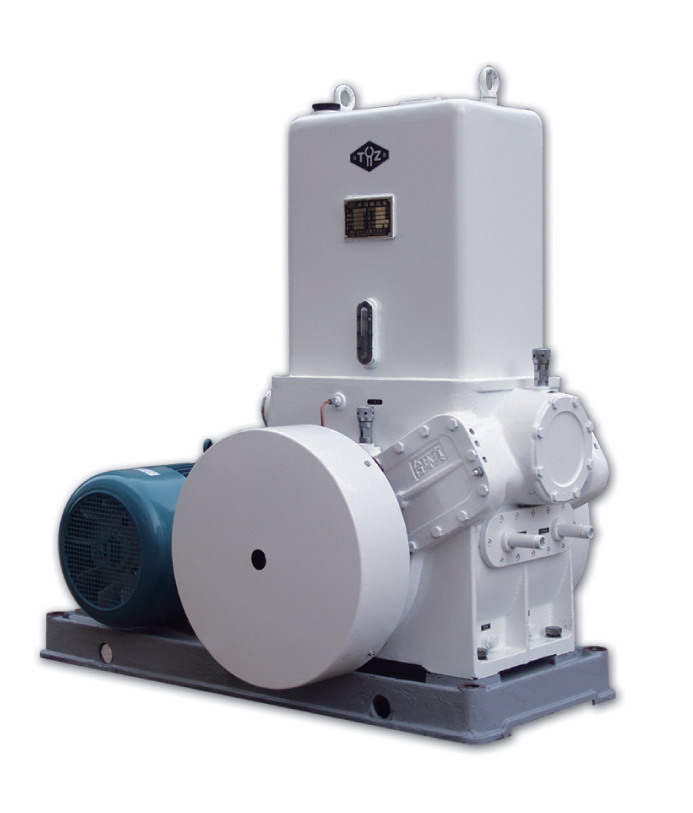

What Are the Key Components of a Piston Vacuum Pump?
A piston vacuum pump consists of several key components that work together to create a vacuum. Here’s a detailed explanation of these components:
1. Cylinder:
– The cylinder is a cylindrical chamber where the piston moves back and forth.
– It provides the housing for the piston and plays a crucial role in creating the vacuum by changing the volume of the chamber.
2. Piston:
– The piston is a movable component that fits inside the cylinder.
– It creates a seal between the piston and cylinder walls, allowing the pump to create a pressure differential and generate a vacuum.
– The piston is typically driven by a motor or an external power source.
3. Intake Valve:
– The intake valve allows gas or air to enter the cylinder during the suction stroke.
– It opens when the piston moves downward, creating a vacuum and drawing gas into the cylinder from the system being evacuated.
4. Exhaust Valve:
– The exhaust valve allows the expelled gas to exit the cylinder during the compression stroke.
– It opens when the piston moves upward, allowing the compressed gas to be expelled from the cylinder.
5. Lubrication System:
– Piston vacuum pumps often incorporate a lubrication system to ensure smooth operation and maintain an airtight seal between the piston and cylinder walls.
– Lubricating oil is introduced into the cylinder to provide lubrication and help maintain the seal.
– The lubrication system also helps to cool the pump by dissipating heat generated during operation.
6. Cooling System:
– Some piston vacuum pumps may include a cooling system to prevent overheating.
– This can involve the circulation of a cooling fluid or the use of cooling fins to dissipate heat generated during operation.
7. Pressure Gauges and Controls:
– Pressure gauges are often installed to monitor the vacuum level or pressure within the system.
– Control mechanisms, such as switches or valves, may be present to regulate the operation of the pump or maintain the desired vacuum level.
8. Motor or Power Source:
– The piston in a piston vacuum pump is typically driven by a motor or an external power source.
– The motor provides the necessary mechanical energy to move the piston back and forth, creating the suction and compression strokes.
9. Frame or Housing:
– The components of the piston vacuum pump are housed within a frame or housing that provides structural support and protection.
– The frame or housing also helps to reduce noise and vibration during operation.
In summary, the key components of a piston vacuum pump include the cylinder, piston, intake valve, exhaust valve, lubrication system, cooling system, pressure gauges and controls, motor or power source, and the frame or housing. These components work together to create a vacuum by reciprocating the piston within the cylinder, allowing gas to be drawn in and expelled, while maintaining an airtight seal. The lubrication and cooling systems, as well as pressure gauges and controls, ensure smooth and efficient operation of the pump.
What Is the Energy Efficiency of Piston Vacuum Pumps?
The energy efficiency of piston vacuum pumps can vary depending on several factors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Design and Technology:
– The design and technology used in piston vacuum pumps can significantly influence their energy efficiency.
– Modern piston pump designs often incorporate features such as optimized valve systems, reduced internal leakage, and improved sealing mechanisms to enhance efficiency.
– Advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques have also contributed to more efficient piston pump designs.
2. Motor Efficiency:
– The motor driving the piston pump plays a crucial role in overall energy efficiency.
– High-efficiency motors, such as those adhering to energy efficiency standards like NEMA Premium or IE3, can significantly improve the energy efficiency of the pump.
– Proper motor sizing and matching to the pump’s load requirements are also important to maximize efficiency.
3. Control Systems:
– The use of advanced control systems can optimize the energy consumption of piston vacuum pumps.
– Variable frequency drives (VFDs) or speed control systems can adjust the pump’s operating speed based on the demand, reducing energy consumption during periods of lower demand.
– Smart control algorithms and sensors can also help optimize the pump’s performance and energy efficiency.
4. System Design and Integration:
– The overall system design and integration of the piston vacuum pump within the application can impact energy efficiency.
– Proper sizing and selection of the pump based on the specific application requirements can ensure that the pump operates within its optimal efficiency range.
– Efficient piping and ducting design, as well as minimizing pressure losses and leaks, can further improve the overall energy efficiency of the system.
5. Load Profile and Operating Conditions:
– The load profile and operating conditions of the piston vacuum pump have a significant impact on energy consumption.
– Higher vacuum levels or flow rates may require more energy to be supplied by the pump.
– Operating the pump continuously at maximum capacity may lead to higher energy consumption compared to intermittent or variable load conditions.
– It’s important to evaluate the specific operating requirements and adjust the pump’s operation accordingly to optimize energy efficiency.
6. Comparing Efficiency Ratings:
– When comparing the energy efficiency of different piston vacuum pumps, it can be helpful to look for efficiency ratings or specifications provided by the manufacturer.
– Some manufacturers provide efficiency data or performance curves indicating the pump’s energy consumption at various operating points.
– These ratings can assist in selecting a pump that meets the desired energy efficiency requirements.
In summary, the energy efficiency of piston vacuum pumps can be influenced by factors such as design and technology, motor efficiency, control systems, system design and integration, load profile, and operating conditions. Considering these factors and evaluating efficiency ratings can help in selecting an energy-efficient piston vacuum pump for a specific application.
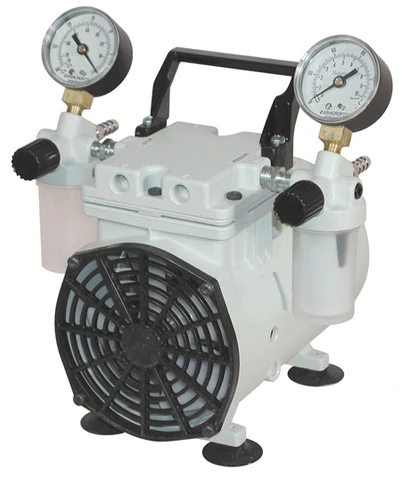

Can Piston Vacuum Pumps Handle Corrosive Gases or Vapors?
Piston vacuum pumps are generally not suitable for handling corrosive gases or vapors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Construction Materials:
– Piston vacuum pumps are typically constructed with materials such as cast iron, aluminum, stainless steel, and various elastomers.
– While these materials offer good resistance to normal operating conditions, they may not be compatible with corrosive substances.
– Corrosive gases or vapors can attack and degrade the pump’s internal components, leading to reduced performance, increased wear, and potential failure.
2. Sealing and Contamination:
– Piston vacuum pumps rely on tight seals and clearances to maintain the vacuum and prevent leakage.
– Corrosive gases or vapors can degrade the seals and compromise their effectiveness.
– This can result in increased leakage, reduced pumping efficiency, and potential contamination of the pump and the surrounding environment.
3. Maintenance and Service:
– Handling corrosive gases or vapors requires specialized knowledge, materials, and maintenance procedures.
– The pump may need additional protective measures, such as corrosion-resistant coatings or specialized seal materials, to withstand the corrosive environment.
– Regular inspection, cleaning, and replacement of components may also be necessary to maintain the pump’s performance and prevent damage.
4. Alternative Pump Options:
– If corrosive gases or vapors are involved in the application, it is advisable to consider alternative pump technologies that are specifically designed to handle such substances.
– For corrosive gases, chemical-resistant pumps like diaphragm pumps, peristaltic pumps, or dry screw pumps may be more suitable.
– These pumps are constructed with materials that offer superior resistance to corrosion and can handle a wide range of corrosive substances.
– It is essential to consult the pump manufacturer or a vacuum system specialist to select the appropriate pump for handling corrosive gases or vapors.
In summary, piston vacuum pumps are generally not recommended for handling corrosive gases or vapors due to their construction materials, sealing limitations, and the potential for damage and contamination. It is crucial to choose a pump specifically designed to handle corrosive substances or consider alternative pump technologies that can provide the required chemical resistance and performance.


editor by CX 2024-04-17