Product Description
China Manufacturer Pump Spare Parts Liner Piston Assembly
Our pistons are strictly manufactured according to API Standard, which with a high performance in various well drilling environment.The hub is forged from high quality steel, and the piston rubber is made from specially formulated compounds which are of heat, oil and water resistance.It is interchangeable with all other API standard designed pistons.
| Product name |
Urethane bonded piston |
||||||
| Material | NBR, Urethane rubber | ||||||
| Length of use | 400-600h | ||||||
| Port | ZheJiang | ||||||
| Application | Water-based drilling fluids | ||||||
Product Parameters
|
Russian pump |
UNBT950,UNB600,8T650,UNBT 1180L,NBT600,NBT300ect. |
|
BOMCO/Emsco/HongHua |
FB1300/1600, F1300/1600, F800/1000, F500 & some duplex pumps. |
|
Gardener denver |
PZ 7, PZ 8/9, PZ 10/11, KF-FXK, FY-FXD, FD-FXX, FG-FXG, FQ-FXQ, FF-FXP, FG-GXG. |
|
National |
7P50, 8P80, 9P100, 10P130, 12P160, 14P220, JWS165, JWS340/400, C250/350, K700, K500, K380. |
|
Oilwell |
A560/600PT, A850/1100PT, A1400/1700PT, 214P, 810P. |
|
Ideco |
T500, T800/1000, T1300/1600. |
|
Wirth |
TPK1000, TPK1600, TPK2000/2200. |
|
Weatherford |
MP-5,MP-8,MP-10,MP-13,MP-16 |
Features, Advantages and Benefits:
This piston is the best choice for oil-based and synthetic drilling fluids.
The piston is bonded to the hub for optimal strength and extrusion resistance.
The improved seal design centers the piston and promotes longer piston life with reduced liner wear.
The cut-back hub protects the liner from damage.
The dual-durometer elastomeric compound resists extrusion while ensuring a tight seal and improved wiping action.
The piston comes complete with a hub O-ring and sleeve.
Factory
Related product:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Manufacturing Process: | Forging |
|---|---|
| Surface Treatment: | Spray-Paint |
| Operation Pressure: | Vacuum |
| Samples: |
US$ 250/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
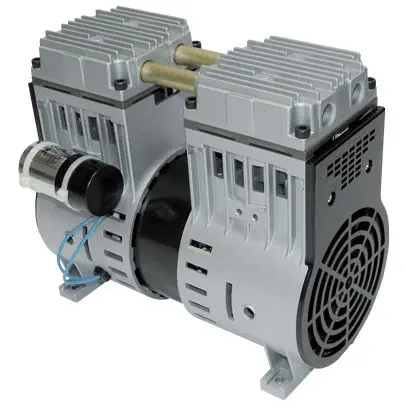

How Does a Piston Vacuum Pump Work?
A piston vacuum pump, also known as a reciprocating vacuum pump, operates using a piston mechanism to create a vacuum. Here’s a detailed explanation of its working principle:
1. Piston and Cylinder Assembly:
– A piston vacuum pump consists of a piston and cylinder assembly.
– The piston is a movable component that fits inside the cylinder and creates a seal between the piston and cylinder walls.
2. Intake and Exhaust Valves:
– The cylinder has two valves: an intake valve and an exhaust valve.
– The intake valve allows gas or air to enter the cylinder during the suction stroke, while the exhaust valve allows the expelled gas to exit during the compression stroke.
3. Suction Stroke:
– During the suction stroke, the piston moves downward, creating a vacuum within the cylinder.
– As the piston moves down, the intake valve opens, allowing gas or air from the system being evacuated to enter the cylinder.
– The volume within the cylinder increases, causing a decrease in pressure and the creation of a partial vacuum.
4. Compression Stroke:
– After the suction stroke, the piston moves upward during the compression stroke.
– As the piston moves up, the intake valve closes, preventing backflow of gas into the evacuated system.
– Simultaneously, the exhaust valve opens, allowing the gas trapped in the cylinder to be expelled.
– The upward movement of the piston reduces the volume within the cylinder, compressing the gas and increasing its pressure.
5. Expulsion of Gas:
– Once the compression stroke is complete, the gas is expelled through the exhaust valve.
– The exhaust valve then closes, ready for the next suction stroke.
– This process of alternating suction and compression strokes continues, gradually reducing the pressure within the evacuated system.
6. Lubrication:
– Piston vacuum pumps require lubrication for smooth operation and to maintain the airtight seal between the piston and cylinder walls.
– Lubricating oil is often introduced into the cylinder to provide lubrication and help maintain the seal.
– The oil also helps to cool the pump by dissipating heat generated during operation.
7. Applications:
– Piston vacuum pumps are commonly used in applications where high vacuum levels and low flow rates are required.
– They are suitable for processes such as laboratory work, vacuum drying, vacuum filtration, and other applications that require moderate vacuum levels.
In summary, a piston vacuum pump operates by creating a vacuum through the reciprocating motion of a piston within a cylinder. The suction stroke creates a vacuum by lowering the pressure within the cylinder, while the compression stroke expels the gas and increases its pressure. This cyclic process continues, gradually reducing the pressure within the system being evacuated. Piston vacuum pumps are commonly used in various applications that require moderate vacuum levels and low flow rates.
What Is the Energy Efficiency of Piston Vacuum Pumps?
The energy efficiency of piston vacuum pumps can vary depending on several factors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Design and Technology:
– The design and technology used in piston vacuum pumps can significantly influence their energy efficiency.
– Modern piston pump designs often incorporate features such as optimized valve systems, reduced internal leakage, and improved sealing mechanisms to enhance efficiency.
– Advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques have also contributed to more efficient piston pump designs.
2. Motor Efficiency:
– The motor driving the piston pump plays a crucial role in overall energy efficiency.
– High-efficiency motors, such as those adhering to energy efficiency standards like NEMA Premium or IE3, can significantly improve the energy efficiency of the pump.
– Proper motor sizing and matching to the pump’s load requirements are also important to maximize efficiency.
3. Control Systems:
– The use of advanced control systems can optimize the energy consumption of piston vacuum pumps.
– Variable frequency drives (VFDs) or speed control systems can adjust the pump’s operating speed based on the demand, reducing energy consumption during periods of lower demand.
– Smart control algorithms and sensors can also help optimize the pump’s performance and energy efficiency.
4. System Design and Integration:
– The overall system design and integration of the piston vacuum pump within the application can impact energy efficiency.
– Proper sizing and selection of the pump based on the specific application requirements can ensure that the pump operates within its optimal efficiency range.
– Efficient piping and ducting design, as well as minimizing pressure losses and leaks, can further improve the overall energy efficiency of the system.
5. Load Profile and Operating Conditions:
– The load profile and operating conditions of the piston vacuum pump have a significant impact on energy consumption.
– Higher vacuum levels or flow rates may require more energy to be supplied by the pump.
– Operating the pump continuously at maximum capacity may lead to higher energy consumption compared to intermittent or variable load conditions.
– It’s important to evaluate the specific operating requirements and adjust the pump’s operation accordingly to optimize energy efficiency.
6. Comparing Efficiency Ratings:
– When comparing the energy efficiency of different piston vacuum pumps, it can be helpful to look for efficiency ratings or specifications provided by the manufacturer.
– Some manufacturers provide efficiency data or performance curves indicating the pump’s energy consumption at various operating points.
– These ratings can assist in selecting a pump that meets the desired energy efficiency requirements.
In summary, the energy efficiency of piston vacuum pumps can be influenced by factors such as design and technology, motor efficiency, control systems, system design and integration, load profile, and operating conditions. Considering these factors and evaluating efficiency ratings can help in selecting an energy-efficient piston vacuum pump for a specific application.

What Is the Role of Lubrication in Piston Vacuum Pump Operation?
Lubrication plays a crucial role in the operation of a piston vacuum pump. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Reduction of Friction:
– Lubrication is essential for reducing friction between moving parts within the pump.
– In a piston vacuum pump, the piston moves up and down inside the cylinder, and lubrication helps to minimize the friction between the piston rings and the cylinder wall.
– By reducing friction, lubrication prevents excessive wear and heat generation, ensuring smooth and efficient operation of the pump.
2. Sealing and Leakage Prevention:
– Lubrication helps to maintain proper sealing between the piston rings and the cylinder wall.
– The lubricating oil forms a thin film between these surfaces, creating a barrier that prevents gas leakage during the compression and vacuum creation process.
– Effective sealing is crucial for maintaining the desired vacuum level and preventing air or gas from entering the pump.
3. Cooling and Heat Dissipation:
– Piston vacuum pumps generate heat during operation, particularly due to the compression of gases.
– Lubricating oil helps in dissipating the heat generated, preventing the pump from overheating.
– The oil absorbs heat from the pump’s internal components and transfers it to the pump’s housing or cooling system.
– Proper cooling and heat dissipation contribute to the pump’s overall performance and prevent damage due to excessive heat buildup.
4. Contaminant Removal:
– Lubrication also aids in removing contaminants or particles that may enter the pump.
– The oil acts as a carrier, trapping and carrying away small particles or debris that could potentially damage the pump’s components.
– The oil passes through filters that help to remove these contaminants, keeping the pump’s internal parts clean and functioning properly.
5. Corrosion Prevention:
– Some lubricating oils contain additives that provide corrosion protection.
– These additives form a protective film on the pump’s internal surfaces, preventing corrosion caused by exposure to moisture or corrosive gases.
– Corrosion prevention is crucial for maintaining the pump’s performance, extending its lifespan, and minimizing the need for repairs or component replacement.
6. Proper Lubrication Selection:
– Selecting the appropriate lubricating oil is essential for the proper functioning of a piston vacuum pump.
– Different pump models and manufacturers may recommend specific oil types or viscosities to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
– It is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding oil selection, oil level, and oil change intervals.
In summary, lubrication plays a vital role in piston vacuum pump operation by reducing friction, maintaining proper sealing, dissipating heat, removing contaminants, and preventing corrosion. Proper lubrication selection and adherence to manufacturer’s guidelines are crucial for ensuring the pump’s efficient and reliable performance.


editor by Dream 2024-04-26